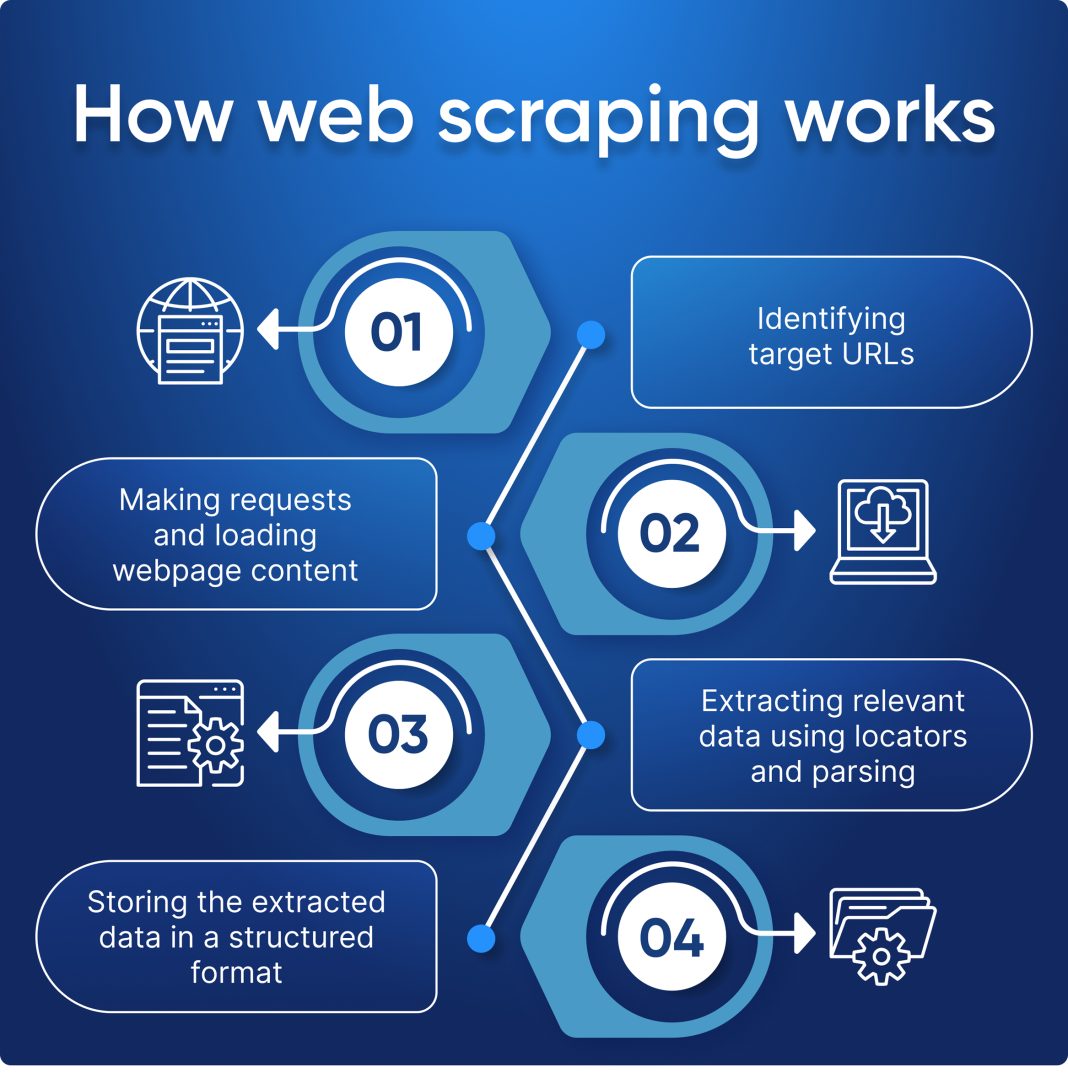
Web scraping is a powerful technique revolutionizing how we gather data from the internet. Byautomatically extracting information from websites, web scraping enables businesses and individuals to compile vast amounts of data efficiently. In this article, we delve into the web scraping fundamentals, exploring essential web scraping tools, as well as the best practices needed for effective data extraction. However, the journey isn’t without its challenges, including dynamic content loading and anti-bot measures. Navigating the ethical landscape of web scraping is crucial, ensuring that data collection adheres to website’s terms and promotes responsible use.
Web data extraction, often referred to as web harvesting or web crawling, has become an indispensable tool for data enthusiasts and organizations alike. This practice involves systematically collecting information from various online sources, making it a key component of data analysis and market research. As we dive deeper into this crucial subject, we will explore the various software applications tailored for data retrieval, highlight best practices in the field, and address the obstacles that frequently arise in the web data extraction process. Furthermore, understanding the ethical implications surrounding web harvesting is essential to maintain integrity and respect for data ownership. Join us as we uncover the intricacies of effectively navigating the world of web data extraction.
Understanding Web Scraping Fundamentals
Web scraping fundamentally transforms how we interact with data on the internet. By leveraging both software and programming languages, individuals can automate the process of gathering information from websites, thus saving time and enhancing productivity. The essence of web scraping lies in the ability to fetch web pages and programmatically retrieve specific data, making it an invaluable tool for businesses, researchers, and developers alike. This automated data extraction facilitates the collection of various types of information, such as product prices, user reviews, and market trends, which can then be analyzed for decision-making purposes.
Understanding the basics of web scraping also involves familiarizing oneself with essential concepts like HTTP requests, HTML structure, and data representation formats like JSON and XML. For those new to web scraping, grasping these fundamentals is critical to successfully deploying scraping tools and scripts. Whether one is using Python libraries or web crawling frameworks, the foundational knowledge in web scraping will empower users to extract and manipulate data effectively.
Essential Web Scraping Tools and Technologies
The landscape of web scraping tools is rich and varied, providing an array of options suited for different needs and skill levels. Popular tools such as Beautiful Soup and Scrapy have gained traction among developers due to their ease of use and versatility. Beautiful Soup is particularly useful for beginners, allowing for quick data extraction from HTML and XML documents. On the other hand, Scrapy is robust and designed for more complex scraping tasks that require efficient handling of multiple pages and sites, making it a favorite among experienced scrapers.
For dynamic websites where data is loaded asynchronously, tools like Selenium and Puppeteer become indispensable. These tools can simulate a user browsing a web page, making it possible to scrape content that might not be available through traditional means. Selenium, for example, can automate a browser session and handle tasks like logging into websites or clicking buttons, providing a seamless scraping experience. When selecting a web scraping tool, it’s important to consider factors like the website’s layout, the complexity of the data, and the scraper’s performance requirements.
Best Practices for Effective Web Scraping
Adhering to best practices is essential in ensuring effective and ethical web scraping. One primary guideline is to respect the ‘robots.txt’ file associated with the website being scraped. This file provides critical information about which parts of a site are permissible for crawlers to access. Ignoring these directives can lead to your scraping activities being blocked or, worse, potential legal ramifications. Additionally, staggering requests over time is crucial to avoid overloading the web server, which can disrupt the website’s normal operations.
Another best practice involves using proper user-agent headers to identify your scraper. Including a user-agent string not only helps in maintaining a good standing with the website but also allows you to access content more reliably. Legitimate scraping activities often involve mimicking human-like behavior, such as managing request intervals and avoiding excessive and rapid requests. By following these best practices, scraper operators can collect data efficiently while minimizing the risk of being classified as malicious bots.
Navigating Common Challenges in Web Scraping
Despite its advantages, web scraping comes with its own set of challenges. One of the most common issues is dealing with dynamic content loading, where websites use JavaScript to render parts of their pages. This can make it difficult for traditional scraping tools, which may only pull static HTML content. To tackle this, scrapers often resort to headless browsers or tools like Selenium that can execute JavaScript and retrieve the rendered HTML, allowing for a more comprehensive data extraction.
Moreover, many websites implement anti-bot measures, including CAPTCHAs and rate-limiting, designed to thwart automated scraping attempts. These challenges necessitate advanced techniques, such as using browser automation for interaction with CAPTCHAs or rotating IP addresses to mitigate detection. Awareness of these challenges is vital as scrapers need to adapt their tactics to maintain access to valuable data while respecting the website’s restrictions.
Ethics of Web Scraping: A Responsible Approach
Ethical considerations in web scraping are critical for both compliance and respect for the data sources. Before initiating a scraping project, it is important to thoroughly review the terms of service of the target websites and ensure that the intended data collection aligns with their guidelines. For instance, certain sites may explicitly prohibit scraping or may allow limited access under specific conditions. Ignoring these ethical standards may not only lead to blocked access but can also result in legal action against the scraper.
Moreover, ethical web scraping involves the responsible use of collected data. This includes safeguarding personal information and adhering to data protection regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe. Always approach data utility and storage with transparency and respect for individuals’ privacy. By promoting ethical practices in web scraping, users contribute to a more sustainable and trust-based internet ecosystem.
Leveraging the Power of Web Scraping Tools
Harnessing web scraping tools effectively can unlock significant insights across industries. For instance, e-commerce businesses can use scraping to monitor competitors’ prices and inventory levels, allowing them to adjust their strategy based on real-time data. By integrating these insights into pricing algorithms, companies can enhance competitiveness and profitability. Furthermore, researchers can gather large datasets for studies that would otherwise require extensive manual effort, accelerating discovery and analysis.
The power of web scraping tools doesn’t just lie in data extraction; it’s also about data transformation and integration into existing systems. With libraries like Pandas in Python, scraped data can be cleaned, analyzed, and visualized effortlessly, providing a complete data processing pipeline. Hence, understanding tool capabilities not only enhances scraping efficiency but also enables users to derive actionable insights that drive decision-making.
Strategies to Overcome Web Scraping Challenges
To successfully navigate the challenges posed by web scraping, developers can employ several strategies. A foundational approach is to design scrapers with adaptability in mind, allowing them to cope with frequently changing web structures and layouts. This might involve writing modular code that can be easily updated or using machine learning algorithms that can learn from changes in website layout automatically. By being proactive in addressing structural changes, developers can significantly prolong the life and effectiveness of their scrapers.
Additionally, incorporating advanced techniques like proxy rotation and headless browsing can help in overcoming challenges such as CAPTCHA and IP blocking. By using a pool of rotating proxies, scrapers can distribute requests across multiple IP addresses, making their activities less detectable. This, combined with user-agent rotation, creates a robust strategy that addresses anti-bot measures and enables seamless data access.
The Future of Web Scraping Technology
As technology evolves, so will web scraping techniques and tools. The continued development of artificial intelligence and machine learning is poised to revolutionize web scraping by making it smarter and more efficient. Algorithms will increasingly be able to understand and adapt to complex website behaviors without human intervention, allowing scrapers to extract data at an unprecedented scale and speed. This future trend may lead to the rise of intelligent scrapers that predict data changes and automate the entire data collection process.
Moreover, the growing focus on ethical data practices will likely influence the future of web scraping technologies. Tools may be developed with built-in compliance checks that help users adhere to legal and ethical standards effortlessly. This integration can ensure that web scraping is conducted responsibly, benefiting both data providers and users. As we look ahead, embracing innovation while maintaining ethical considerations will be crucial for fostering a healthy ecosystem for web scraping.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the fundamental concepts of web scraping?
The fundamentals of web scraping involve understanding how to automatically extract data from websites by fetching web pages and parsing the HTML. Key components include selecting the right web scraping tools, like Beautiful Soup or Scrapy, and familiarizing yourself with the HTML structure of web pages to locate and extract desired data.
What are the best tools for web scraping?
When considering web scraping tools, some of the best options include Beautiful Soup for HTML parsing in Python, Scrapy for comprehensive web crawling tasks, Selenium for simulating browser interactions, and Puppeteer for controlling headless Chrome. Each tool offers unique capabilities suited for different web scraping requirements.
What are some best practices for ethical web scraping?
To practice ethical web scraping, it’s essential to respect a website’s `robots.txt` file, which indicates which areas are off-limits for scraping. Additionally, avoid overloading a server with excessive requests, use appropriate user-agent headers, and always review a website’s terms of service before beginning any scraping project.
What challenges can arise when performing web scraping?
Common challenges of web scraping include handling dynamic content that loads via JavaScript, which can complicate data extraction. Other difficulties may include bypassing anti-bot measures such as CAPTCHAs and rate limiting, which are designed to prevent excessive scraping activities. Understanding how to tackle these challenges is key to successful web scraping.
How can I ensure I am following web scraping best practices?
To follow web scraping best practices, start by reviewing a site’s `robots.txt` file and adhere to it. Limit the number of requests made in a given timeframe to prevent server overload, and use proper user-agent headers to identify your scraper. Also, consider implementing delays between requests to mimic human browsing behavior.
What are the ethical considerations involved in web scraping?
Ethical web scraping entails respecting copyright laws, adhering to a website’s terms of service, and ensuring that the data collected is not misused. Always aim for transparency and accountability when scraping data, and mitigate any potential harm to the source website or its users.
| Key Point | Description |
|---|---|
| What is Web Scraping? | The process of automatically extracting information from websites and fetching web pages to obtain data using various tools. |
| Tools for Web Scraping | Popular tools include Beautiful Soup, Scrapy, Selenium, and Puppeteer, each serving different needs for data extraction. |
| Best Practices | Respect `robots.txt`, limit requests to avoid server overload, and use appropriate user-agent headers. |
| Common Challenges | Dynamic content loading and anti-bot measures like Captchas can complicate data extraction. |
| Ethics of Web Scraping | Scrapers should review terms of service and ensure responsible use of the data they collect. |
Summary
Web scraping is an essential technique for extracting information from websites efficiently. By employing the right tools, adhering to best practices, and ethical guidelines, individuals and organizations can leverage web scraping to gather valuable data for various applications. From understanding the fundamentals to overcoming common challenges, mastering web scraping opens up a world of possibilities for data-driven decision-making and analysis.