Machine learning is a transformative branch of artificial intelligence that empowers systems to learn from data, thus making informed predictions or decisions without explicit programming. This innovative approach encompasses various types of machine learning, such as supervised and unsupervised learning, each serving unique applications across industries. From enhancing email filtering to powering medical diagnosis, the diverse applications of machine learning reveal its profound impact on our daily lives. However, the field is not without its challenges, including data privacy concerns and model bias, which must be addressed to fully leverage its capabilities. Understanding machine learning is essential for embracing its potential and navigating its complexities, making it a key area of focus in modern technology.
Artificial intelligence’s subset, often referred to as predictive analytics or intelligent algorithms, focuses on the development of systems that can autonomously learn from vast amounts of information. This domain includes various methodologies, such as algorithmic training and data clustering, which allow machines to distill complex data into actionable insights. With applications spanning from self-driving vehicles to stock market forecasting, the importance of these predictive systems cannot be understated. Yet, as we explore this fascinating field, it is crucial to remain cognizant of the hurdles that persist, such as the need for secure data management and the mitigation of inherent biases in model training. A comprehensive understanding of this digital intelligence realm will equip us to maximize its benefits while minimizing risks.
Introduction to Machine Learning Concepts
Machine learning, a subfield of artificial intelligence (AI), has gained significant attention over the past few decades. It revolves around the idea that systems can learn from data, improve their performance, and make decisions with minimal human intervention. Understanding the fundamentals of machine learning is essential for anyone looking to delve into this innovative discipline. The field combines insights from computer science, statistics, and domain-specific knowledge, enabling machines to recognize patterns and draw conclusions based on the data they process.
As we dive deeper into machine learning, we find that it not only revolutionizes how we analyze data but also enhances decision-making processes across various industries. From predictive analytics to automation, machine learning simplifies complex tasks and amplifies the capabilities of traditional computational techniques. By grasping the core concepts, principles, and applications of machine learning, one can better appreciate its transformative potential in today’s data-driven world.
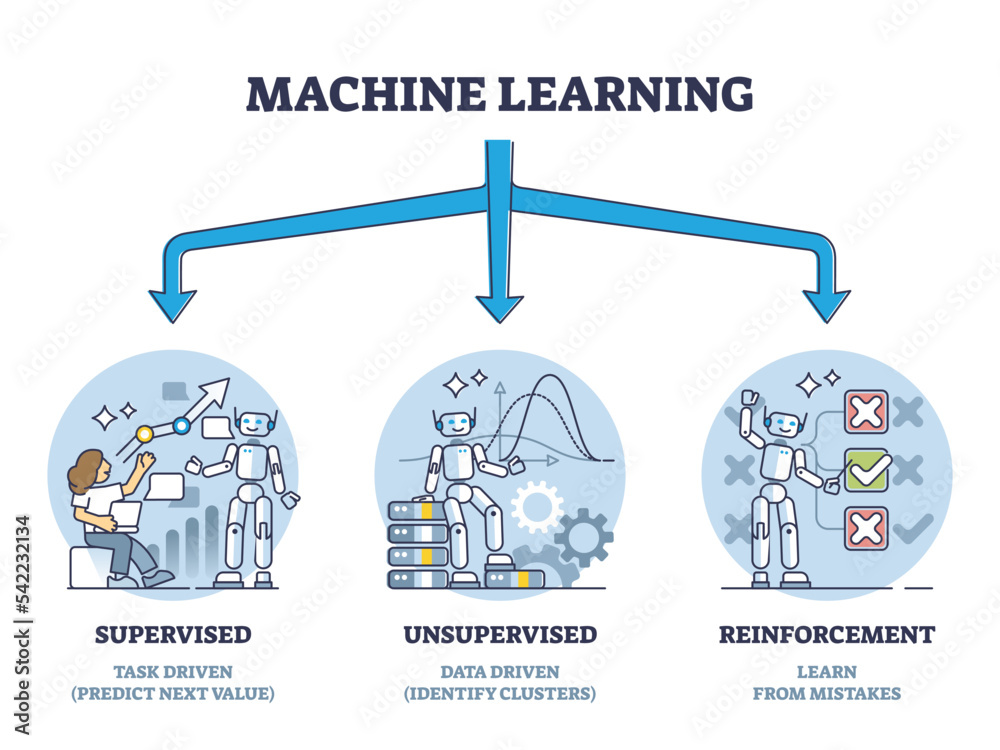
Exploring Types of Machine Learning
When discussing types of machine learning, we primarily recognize three major categories: supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning. Supervised learning utilizes labeled datasets, where the model learns to predict outcomes based on input features. This method finds applications in fields such as email filtering and medical diagnosis, where known labels guide the training process. The robustness of supervised learning models lies in their ability to generalize well to unseen data, but they require comprehensive labeled datasets for optimal performance.
Conversely, unsupervised learning tackles scenarios where the data lacks explicit labels. In such cases, algorithms are designed to identify patterns and inherent structures within datasets. Common techniques include clustering and dimensionality reduction. Unsupervised learning is particularly useful in customer segmentation and market basket analysis, revealing valuable insights that drive strategic business decisions. Reinforcement learning adds another layer by enabling agents to learn from their environment through trial and error, optimizing their actions based on cumulative rewards.
The Multifaceted Applications of Machine Learning
Machine learning applications are vast and varied, spanning industries from healthcare to finance. For instance, in the realm of healthcare, machine learning algorithms facilitate medical diagnosis by analyzing patient data and identifying potential ailments. Additionally, machine learning plays a crucial role in developing autonomous systems, such as self-driving cars. By making real-time decisions based on environmental data input, these systems enhance safety and efficiency, illustrating the practical implications of machine learning in real-world scenarios.
In finance, machine learning algorithms are employed for algorithmic trading, where they process massive datasets to predict stock market trends. Other applications include fraud detection, sentiment analysis, and customer service automation. The versatility of machine learning opens avenues for innovation, enabling organizations to optimize operations, enhance user experiences, and gain a competitive edge in their respective markets.
Addressing Challenges in Machine Learning
Despite its remarkable advantages, machine learning isn’t free from challenges. One primary concern is data privacy, particularly in sensitive areas like healthcare and finance, where personal information is at stake. Organizations must implement stringent protocols to safeguard user data while utilizing machine learning algorithms. Additionally, issues such as model overfitting and underfitting complicate the development process, leading to unreliable predictions if not addressed adequately.
Bias in training datasets also poses a significant challenge, potentially leading to inaccurate and unfair outcomes for certain demographics. Therefore, it’s crucial for data scientists and machine learning engineers to be vigilant about the data their models are trained on. Moreover, the interpretability of machine learning models can be a barrier to trust and acceptance among stakeholders, as complex algorithms may produce predictions without transparent explanations. Hence, overcoming these challenges is vital for leveraging machine learning’s full potential.
Concluding Insights on Machine Learning
In conclusion, machine learning represents a dynamic and rapidly evolving field that is set to reshape the future of technology and industry. Its ability to extract insights from vast amounts of data enables organizations to make informed decisions and enhance operational efficiency. By understanding the various types of machine learning, their applications, and the challenges involved, stakeholders can better navigate this complex landscape.
As machine learning continues to advance, embracing its transformative power while remaining aware of ethical considerations will be key to its successful integration in society. By harnessing the full potential of machine learning, we can unlock new possibilities and innovations that drive progress across all sectors.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main types of machine learning?
The main types of machine learning include supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning. Supervised learning uses labeled datasets to train models, while unsupervised learning analyzes unlabeled data to discover patterns. Reinforcement learning trains agents to make decisions based on rewards from their actions.
What are some common applications of machine learning?
Machine learning is utilized in various applications such as email filtering to detect spam, image and speech recognition, aiding in self-driving car technology, enhancing medical diagnoses, and forecasting stock market trends.
What challenges are associated with machine learning?
Challenges in machine learning include data privacy issues, overfitting and underfitting of models, potential bias in training data, and difficulties in model interpretability. Addressing these challenges is critical for effective machine learning implementations.
How does supervised learning differ from unsupervised learning in machine learning?
Supervised learning involves training models on labeled datasets, where outputs are known, allowing for predictive accuracy. In contrast, unsupervised learning deals with unlabeled data, aiming to identify inherent structures or patterns without predefined outcomes.
How can understanding machine learning improve business decisions?
Understanding machine learning can significantly enhance business decisions by leveraging predictive analytics and data-driven insights, allowing companies to optimize operations, personalize customer experiences, and identify trends in market behavior.
| Key Point | Description |
|---|---|
| What is Machine Learning? | A field of artificial intelligence that develops algorithms for computers to learn from data and make predictions or decisions. |
| Types of Machine Learning | 1. Supervised Learning: Uses labeled datasets for training. 2. Unsupervised Learning: Works with unlabeled data to find patterns. 3. Reinforcement Learning: Trains agents to maximize rewards through actions. |
| Applications of Machine Learning | Used in various fields for tasks such as email filtering, image and speech recognition, self-driving cars, medical diagnosis, and stock market predictions. |
| Challenges in Machine Learning | Includes data privacy issues, overfitting and underfitting, bias in training data, and challenges in model interpretability. |
| Conclusion | Understanding the principles, types, applications, and challenges of machine learning is essential to fully leverage its capabilities. |
Summary
Machine learning is a dynamic and transformative field within artificial intelligence, empowering computers to learn from data and improve their performance over time. By grasping its core principles, diverse types, real-world applications, and inherent challenges, individuals and organizations can better utilize machine learning to solve complex problems and drive innovation.