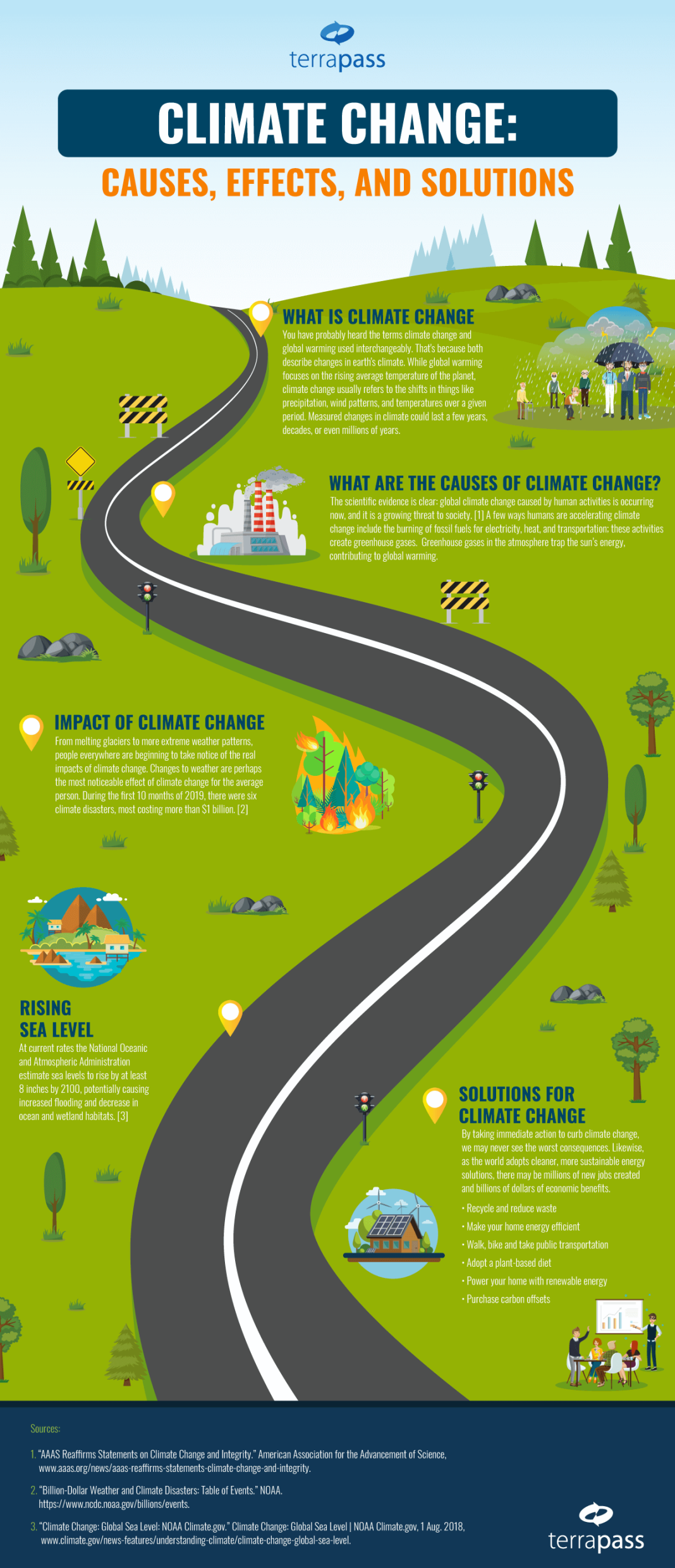
Climate change is an urgent global challenge that threatens our planet’s climate systems, exposing ecosystems and communities to profound changes. The primary causes of climate change stem from human activities, particularly the burning of fossil fuels, deforestation, and certain agricultural practices that release greenhouse gases. These emissions not only heat our atmosphere but also contribute to devastating effects such as extreme weather events, rising sea levels, and biodiversity loss. As we delve into the science behind climate change, it is imperative to explore effective mitigation strategies, including the transition to renewable energy resources. By understanding the causes and effects of climate change, we can foster impactful solutions that promote sustainability and resilience for future generations.
The phenomenon of global warming, often recognized as climate change, encompasses significant shifts in weather patterns and environmental conditions on Earth. This escalating crisis results from various anthropogenic factors that exacerbate the greenhouse effect, primarily through fossil fuel combustion and land-use changes. The repercussions of such alterations are widespread, leading to catastrophic weather extremes and the degradation of natural habitats. Addressing this critical issue requires robust climate science to inform sustainable practices and renewable energy adoption, thus mitigating the impacts of global warming. Engaging with this multifaceted topic is essential for understanding our collective responsibility in fostering a healthier planet.
Exploring the Major Causes of Climate Change
Climate change is primarily driven by human activities that release significant amounts of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. The burning of fossil fuels—such as coal, oil, and natural gas—stands as one of the most significant contributors. This process not only emits large volumes of carbon dioxide (CO2), which is a principal greenhouse gas, but it also contributes to air pollution and environmental degradation. Deforestation is another major cause; as trees are cut down for agriculture and urbanization, the natural ability of forests to absorb CO2 diminishes. Furthermore, the destruction of habitats through logging releases CO2 stored in the trees, exacerbating the greenhouse effect and accelerating climate change.
Agricultural practices also play a crucial role in climate change. Modern farming techniques—such as the use of synthetic fertilizers—result in the release of nitrous oxide, another potent greenhouse gas. Livestock farming contributes significantly to methane emissions, a gas far more effective at trapping heat in the atmosphere than CO2. The interplay of these various activities underscores the need for systemic changes in how we generate energy and produce food, both to mitigate climate change and to promote sustainability.
Understanding the Effects of Climate Change
The impacts of climate change are far-reaching and can severely disrupt natural ecosystems and human societies alike. Notably, the increasing frequency of extreme weather events poses significant challenges; hurricanes, wildfires, and droughts are becoming more common and intense, leading to devastating effects on agriculture, infrastructure, and human safety. Additionally, as global temperatures rise, glaciers and polar ice caps melt, leading to rising sea levels that threaten coastal communities around the world. These tangible effects underscore the urgent need for action to address the changing climate.
One of the more insidious consequences of climate change is ocean acidification, which occurs as oceans absorb excess CO2 from the atmosphere. This alteration in ocean chemistry can lead to the collapse of marine ecosystems, affecting everything from plankton to larger species like fish and marine mammals. The disruption of these ecosystems can have cascading effects on global food chains and biodiversity. Understanding these effects is crucial for promoting informed discussions and policies aimed at addressing climate change at both local and global levels.
Adopting Effective Mitigation Strategies for Climate Change RESPONSE: Fast-tracking sustainable solutions is essential if we aim to mitigate climate change effectively. Transitioning to renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydroelectric power not only reduces CO2 emissions significantly but also presents an opportunity to create sustainable energy systems that can support economic growth. Investment in renewable technology promotes energy independence and reduces reliance on fossil fuels; hence, adopting these resources can lead to a gradual decarbonization of various sectors.
Moreover, enhancing energy efficiency in buildings and transportation is a critical strategy for reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Simple measures such as better insulation, energy-efficient appliances, and the adoption of electric vehicles can lead to substantial CO2 reductions. Additionally, promoting reforestation and sustainable land practices ensures a more effective carbon sink, which is crucial for offsetting emissions. Implementing these strategies will not only help combat climate change but also foster a healthier planet for future generations.
The Importance of Climate Change Science in Policy-Making RESPONSE: Understanding the science behind climate change is paramount for formulating effective policies and actions. Climate change science delves into the mechanisms of greenhouse gas emissions and their impact on global temperatures. By incorporating scientific research into policymaking, governments and organizations can devise more effective strategies to combat climate change, ensuring that actions are based on evidence rather than conjecture.
Furthermore, as public awareness of climate change grows, it becomes increasingly important to communicate the science effectively to the broader audience. Engaging the public through education and outreach fosters a better understanding of the challenges posed by climate change, galvanizing community support for policy changes and sustainable practices. Engaging stakeholders—including businesses, non-profit organizations, and the public—paves the way for collaborative efforts to combat climate change effectively and comprehensively.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main causes of climate change?
The main causes of climate change include the burning of fossil fuels like coal, oil, and gas, which release large amounts of carbon dioxide (CO2) into the atmosphere. Deforestation also contributes to climate change by reducing the number of trees that can absorb CO2. Additionally, certain agricultural practices release methane and nitrous oxide, further exacerbating the problem.
How does climate change affect weather patterns?
Climate change significantly impacts weather patterns, increasing the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events such as hurricanes, droughts, and heatwaves. These changes disrupt normal climatic conditions, leading to devastating effects on ecosystems and human communities.
What are the effects of climate change on sea levels?
One of the major effects of climate change is the rising sea levels resulting from the melting of glaciers and polar ice. As temperatures rise, the increased volume of water contributes to coastal flooding, threatening habitats and human settlements in low-lying areas.
What mitigation strategies are effective against climate change?
Effective mitigation strategies against climate change include transitioning to renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power. Implementing energy efficiency measures in homes and transportation, as well as promoting reforestation and sustainable agricultural practices, are also critical in reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
How does renewable energy impact climate change?
Renewable energy plays a crucial role in combating climate change by significantly reducing greenhouse gas emissions when compared to fossil fuels. By harnessing energy from natural resources such as sunlight, wind, and water, we can decrease our reliance on carbon-intensive energy sources, thereby mitigating the adverse effects of climate change.
What is the science behind climate change?
The science behind climate change involves understanding how human-induced activities, particularly the emission of greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide (CO2), are altering the Earth’s climate system. These gases trap heat in the atmosphere, leading to global warming and subsequent changes in climate patterns.
What is the role of deforestation in climate change?
Deforestation is a significant driver of climate change as it involves cutting down trees that absorb carbon dioxide (CO2). This not only reduces the planet’s capacity to sequester carbon but also releases stored CO2 back into the atmosphere, contributing to the greenhouse effect and climate warming.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition of Climate Change | Long-term changes in temperature, precipitation, winds, and other climate factors, primarily due to human activities. |
| Causes of Climate Change | 1. Burning Fossil Fuels: Increases CO2 emissions. 2. Deforestation: Reduces CO2 absorption. 3. Agricultural Practices: Emits methane and nitrous oxide. |
| Effects of Climate Change | 1. Severe weather events (hurricanes, droughts). 2. Rising sea levels due to melting ice. 3. Ecosystem disruptions leading to biodiversity loss. |
| Mitigation Strategies | 1. Transition to renewable energy (wind, solar). 2. Improve energy efficiency in transportation/buildings. 3. Promote reforestation and sustainable practices. |
Summary
Climate change is a pressing global issue that demands immediate attention. The scientific understanding of climate change highlights the multifaceted causes, including human-induced greenhouse gas emissions and deforestation. The alarming effects, such as extreme weather events and rising sea levels, pose significant challenges to ecosystems and human communities. Implementing effective mitigation strategies, such as transitioning to renewable energy and enhancing energy efficiency, is crucial in combating climate change. With collective global action, meaningful progress can be achieved to address this urgent crisis.