Machine learning, a powerful subset of artificial intelligence, revolutionizes the way systems learn from data, identify patterns, and make decisions with minimal human oversight. By leveraging various machine learning types, including supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning, organizations can harness insights that were previously unimaginable. The applications of machine learning are vast, ranging from enhancing healthcare through predictive analytics to improving financial risk assessments and targeted marketing strategies. As more industries recognize the significance of machine learning, the demand for skilled professionals in this field continues to grow. Understanding the fundamentals of machine learning is crucial for anyone looking to thrive in our increasingly data-driven world.
Artificial intelligence techniques like data-driven learning have emerged as essential tools for modern technology, often referred to collectively as machine learning. This category of algorithms encompasses various approaches, such as training on labeled datasets in supervised learning, exploring data structures in unsupervised learning, and decision-making through reinforcement learning. The versatility of these techniques allows for diverse applications, helping businesses and sectors gain insights and efficiencies previously unattainable. From predicting health outcomes to optimizing marketing campaigns, the impact of machine learning is profound. Gaining knowledge of these concepts is vital for those wishing to navigate the future landscape shaped by intelligent systems.
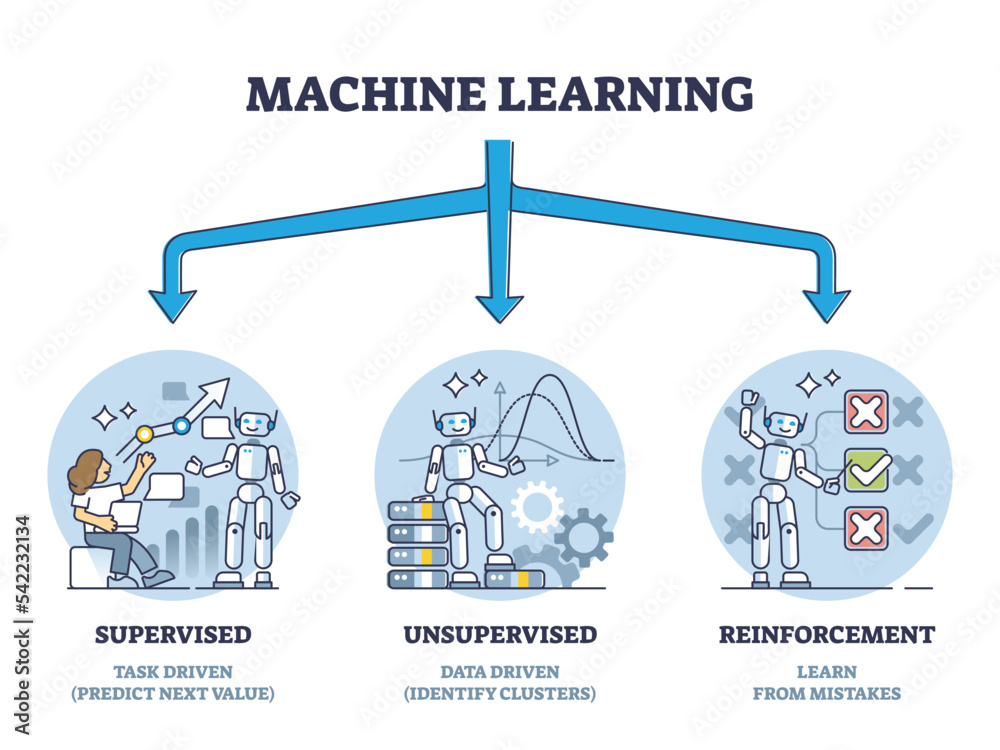
Exploring the Types of Machine Learning
Machine learning can be broadly categorized into three main types: supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning. Supervised learning involves using labeled datasets where the model learns predictions by mapping input data to their respective correct outputs. This approach is widely used in applications such as classification, where the model is trained to recognize different categories based on provided examples. Common algorithms like decision trees, support vector machines, and neural networks fall under this category.
In contrast, unsupervised learning deals with data that does not have labels. This allows models to analyze the intrinsic structure of data without prior knowledge of the outcomes. Clustering and association are key techniques in this domain, commonly utilized for tasks such as customer segmentation and discovering correlations within datasets. Another type, reinforcement learning, focuses on training agents to make sequential decisions by interacting with an environment, effectively learning from the success or failure of previous actions to maximize cumulative rewards.
Significance of Machine Learning Applications
The applications of machine learning span a diverse array of sectors, significantly impacting how industries operate. In healthcare, machine learning algorithms analyze vast datasets to predict patient outcomes, improve diagnostic accuracy, and develop personalized treatment plans tailored to individual patient needs. This predictive capability not only enhances patient care but also streamlines operational efficiency within healthcare facilities.
Similarly, the finance sector benefits greatly from machine learning applications through enhanced fraud detection and risk assessment models. By employing algorithms that can process transaction data in real-time, financial institutions can identify and respond to fraudulent activities more swiftly. In marketing, machine learning aids in customer segmentation for more effective targeted advertising campaigns, thereby increasing customer engagement and driving sales. These advancements highlight the transformative potential of machine learning technologies across various industries.
The Future of Machine Learning in Industries
As machine learning technology continues to evolve, its influence on various sectors is poised to grow exponentially. Businesses are increasingly recognizing the benefits of integrating machine learning into their operations to drive innovation and achieve competitive advantages. This shift is not only about automating tasks but also involves leveraging data analytics to derive insights that were previously unattainable, paving the way for more informed decision-making.
Looking ahead, the future of machine learning appears bright, as emerging technologies like deep learning and natural language processing further enhance its capabilities. Industries such as autonomous vehicles, smart manufacturing, and natural language processing are expected to benefit immensely from these advancements. By investing in machine learning, organizations are not only preparing for the future but are also setting the stage for groundbreaking developments that could redefine industry standards.
Machine Learning: A Game Changer in Technology
Machine learning is often hailed as a game-changer in technology due to its ability to create systems that can learn and adapt independently. The implication of this capability is profound; companies can harness large volumes of data to train models that improve over time, leading to increased efficiency and reduced operational costs. Whether it’s through predictive analytics in business intelligence or recommendation systems in e-commerce, machine learning is integral to driving technological advancement.
Moreover, the intersection of machine learning with other areas such as the Internet of Things (IoT) further amplifies its impact. Devices equipped with machine learning algorithms can analyze real-time data, contribute to smarter decision-making, and ultimately enhance user experiences. This integration is indicative of a future where machine learning will be central to the operation of various technologies, ranging from personal devices to industrial machines.
Understanding Supervised Learning
Supervised learning is a cornerstone of machine learning, characterized by its reliance on labeled datasets. In this process, algorithms are trained using input-output pairs, allowing them to learn the mapping between the data features and the expected outcomes. This method is particularly effective for classification tasks, where the goal is to assign inputs to predefined categories. Algorithms such as logistic regression and neural networks exemplify the supervised learning technique.
One of the primary advantages of supervised learning is its ability to produce highly accurate models, as the training process is guided by known outputs. This makes it invaluable in domains like predictive maintenance, where precisely predicting equipment failures can lead to significant cost savings and improved performance. However, the effectiveness of supervised learning heavily relies on the quality and quantity of the labeled data available, which can sometimes pose a challenge when dealing with large and complex datasets.
Unraveling Unsupervised Learning
Unsupervised learning contrasts sharply with supervised learning, as it deals with datasets that lack explicit labels. This approach allows algorithms to uncover hidden patterns within the data, making it invaluable for exploratory data analysis and feature discovery. Techniques such as clustering and dimensionality reduction are frequently used in unsupervised learning to group similar data points and simplify complex datasets, respectively.
A notable application of unsupervised learning can be found in customer segmentation. Businesses utilize this technique to identify distinct customer groups based on purchasing behavior or preferences, enabling more tailored marketing strategies. As companies increasingly recognize the diversity in consumer behavior, unsupervised learning becomes a vital tool for deriving actionable insights from unstructured data, ultimately enhancing customer experiences and driving revenue.
Harnessing the Power of Reinforcement Learning
Reinforcement learning is a subset of machine learning that focuses on developing algorithms that learn optimal actions through trial and error. This learning paradigm employs a reward-based system where an agent receives feedback as it interacts with its environment. Over time, the agent learns to take actions that maximize the cumulative rewards, making reinforcement learning suitable for dynamic environments where decision-making is critical.
Applications of reinforcement learning are evident in areas such as robotics, gaming, and autonomous systems. For instance, in robotics, reinforcement learning can train robots to navigate complex environments effectively, learn to perform tasks, and adapt to new challenges. In gaming, reinforcement learning has been successfully employed to develop AI that can outplay human participants in complex strategy games, showcasing its potential to revolutionize how we approach problem-solving in uncertain scenarios.
The Importance of Data in Machine Learning
Data is the lifeblood of machine learning models, as these systems rely on vast amounts of information to learn and make predictions. The quality and relevance of data directly influence the model’s performance and accuracy. Collecting, cleaning, and preprocessing data to ensure it is free from biases or errors is a critical step in the machine learning workflow. By utilizing robust datasets, organizations can enhance the reliability of their models and generate trustworthy predictions.
As machine learning continues to permeate various industries, the emphasis on data governance and ethical data practices becomes increasingly vital. Ensuring that data is collected and utilized responsibly, with respect for privacy and consent, is paramount. Educational initiatives focusing on data literacy can empower organizations to harness machine learning effectively, thus ensuring that data serves as a catalyst for positive change in society.
Machine Learning Trends to Watch
Keeping up with trends in machine learning is essential for businesses looking to stay competitive. Current trends include the growing importance of explainable AI, which focuses on making model outputs interpretable for users. This trend is essential, especially in sectors like healthcare and finance, where understanding how decisions are made can have significant implications for trust and accountability.
Additionally, advancements in transfer learning are making it easier to apply pre-trained models to new but related problems, reducing the time and resources needed for data preparation. This trend allows organizations to innovate faster, leveraging existing models and refining them for specific applications. Embracing these and other emerging trends in machine learning positions businesses favorably in an increasingly data-driven world.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the different types of machine learning?
The main types of machine learning include supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning. Supervised learning involves training a model with labeled data, unsupervised learning identifies patterns in unlabeled data, and reinforcement learning focuses on training agents to optimize their actions in an environment for maximum rewards.
How is supervised learning used in machine learning applications?
Supervised learning is widely used in machine learning applications such as spam detection in email services, image recognition, and medical diagnosis, where the model learns from labeled datasets to make accurate predictions or classifications.
What is unsupervised learning, and where can it be applied?
Unsupervised learning is a type of machine learning that deals with unlabeled data, allowing models to find hidden patterns or groupings. It is applied in market segmentation, customer behavior analysis, and anomaly detection, helping businesses uncover insights without prior labeling of the data.
What role does reinforcement learning play in machine learning?
Reinforcement learning is crucial in machine learning for developing systems that learn through trial and error. It is commonly used in robotics, gaming, and autonomous vehicles, where agents learn to make decisions based on rewards from their actions in complex environments.
What are some common applications of machine learning in healthcare?
In healthcare, machine learning applications include predictive analytics for patient outcomes, personalized treatment plans based on patient data, and diagnostic tools that assist doctors in identifying diseases more accurately.
How does machine learning contribute to advancements in finance?
Machine learning enhances finance through applications such as fraud detection, credit scoring, algorithmic trading, and risk assessment in investments. By analyzing vast amounts of financial data, machine learning models can identify trends and make informed predictions.
What is the significance of machine learning in marketing?
Machine learning transforms marketing by enabling customer segmentation, improving targeted advertising campaigns, and analyzing consumer behavior. By utilizing data-driven insights, businesses can create more effective marketing strategies tailored to specific audiences.
| Key Points | Description |
|---|---|
| Machine Learning | A subset of artificial intelligence allowing systems to learn from data and make decisions with minimal human intervention. |
| Types of Machine Learning | Includes Supervised Learning, Unsupervised Learning, and Reinforcement Learning. |
| Applications in Healthcare | Predictive analytics for patient outcomes and personalized treatment. |
| Applications in Finance | Fraud detection and risk assessment in investments. |
| Applications in Marketing | Customer segmentation and targeted advertising. |
Summary
Machine Learning is a driving force behind the advancement of technology and various industries. By enabling systems to analyze and learn from data, it creates opportunities for enhanced decision-making and efficiency. Its applications range from healthcare improvements to fraud detection in finance, showcasing its transformative potential across different sectors. As we delve deeper into the capabilities of machine learning, staying informed about its principles becomes crucial for optimizing its use in real-world scenarios.