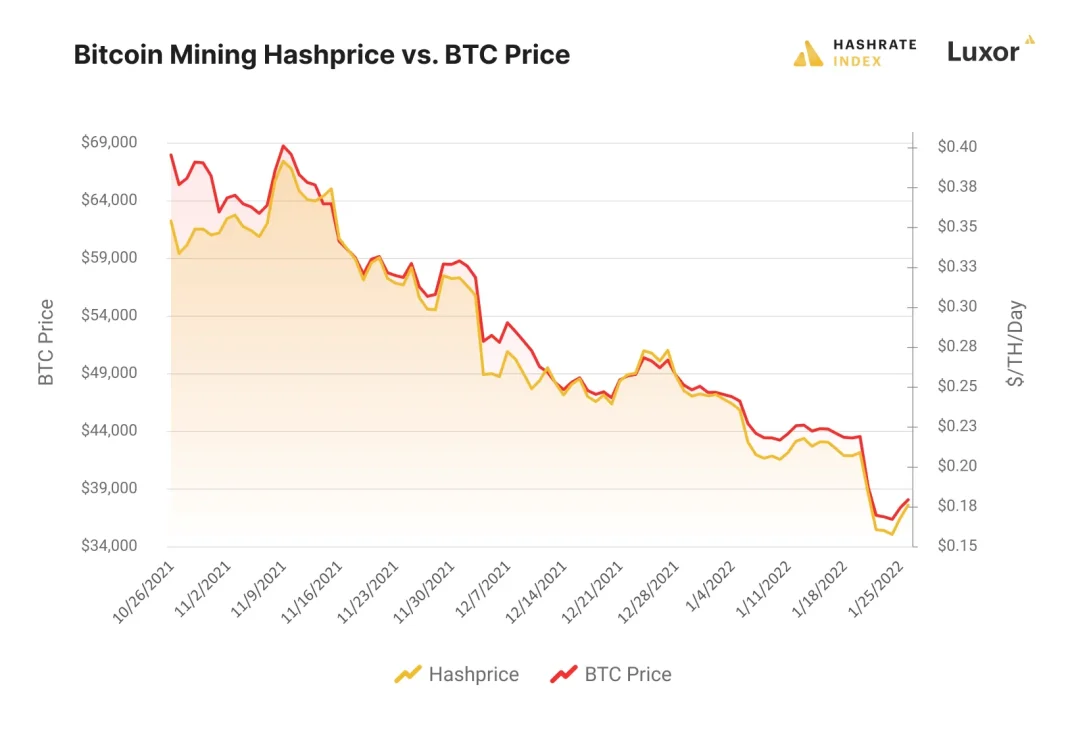
The recent decline in Bitcoin hashprice has sent shockwaves through the cryptocurrency mining industry, as the daily expected value of hashing power hits an all-time low. This downturn is significantly impacting mining revenue and Bitcoin mining profitability, creating urgent challenges for miners across the globe. Contributing factors such as the halving effects in 2020 and 2024, combined with diminished blockchain fees, have compounded the situation. Today, miners face the reality that only a fraction of their rewards comes from transaction fees, while the value of petahash continues to plummet. As the ecosystem grapples with these hurdles, it’s clear that urgent measures are needed to sustain operations and prevent further financial strain on miners.
The ongoing crisis in the realm of Bitcoin hashvalue exemplifies the broader challenges facing cryptocurrency miners today. With the revenues from mining dwindling, terms like digital asset extraction and profitability in blockchain ventures are becoming increasingly relevant. The repercussions of the recent halvings, which effectively reduce mining rewards, coupled with a drop in transaction fee income, have placed strain on miners’ economic viability. Moreover, the diminishing returns from each petahash are forcing many to reevaluate their strategies or explore innovations like AI-enhanced mining operations. As market conditions evolve, the need for adaptive solutions to enhance revenue generation becomes more apparent.
Understanding Bitcoin Hashprice Decline
Bitcoin’s hashprice decline reflects a broader trend in the mining industry, notably tied to historical events like the halvings. The halving events, such as those in May 2020 and anticipated in 2024, cut the block reward miners earn for validating transactions. This not only reduces the immediate payouts for miners but also places pressure on the overall mining revenue. The result is a significant drop in the expected daily value of hashing power, leading to a record low hashprice as miners receive less compensation for their efforts, despite the ever-increasing cost of electricity and hardware.
Moreover, the sustainability of mining becomes questionable as Bitcoin’s price fluctuates. As of November 2025, even with a relatively high Bitcoin price, the hashprice has plummeted, indicating that the profitability of Bitcoin mining is increasingly challenged. The decline of hashprice will compel miners to examine their operational efficiencies, upgrade equipment, or explore diverse avenues for income, thus reshaping the entire mining landscape.
Impacts of Halvings on Bitcoin Mining Profitability
The halving events play a pivotal role in Bitcoin mining profitability, acting as a double-edged sword. While they contribute to Bitcoin’s scarcity — a fundamental tenet that drives value — they inadvertently create fluctuations in mining profitability. For example, post-halving periods often see a surge in Bitcoin prices, but they also lead to an immediate decrease in rewards for miners, as illustrated by the transition from a 6.25 BTC to a 3.125 BTC reward in 2020. Miners have to balance their operational costs against the reduced rewards to maintain profitability.
Furthermore, the aftermath of a halving often results in a period where on-chain activity and transaction fees don’t compensate for the lost block rewards. Consequently, as transaction fees become a smaller share of miner revenues — only around 0.73% currently — miners must adapt to a world where increasing hashpower does not yield proportional profits. As a result, they may need to innovate and adopt new technologies or strategies to enhance their chances of remaining profitable.
Role of Blockchain Fees in Mining Revenue Decline
Blockchain fees are an essential component of mining revenue, yet their sharp decline complicates the landscape for Bitcoin miners. Since block rewards are halved, miners have become increasingly reliant on transaction fees to supplement their revenue. However, as the crypto market matures and competition increases, the fees associated with transactions have dwindled. This lack of substantial fees is jeopardizing the economic viability of many mining operations, leading to an intensifying scrutiny of operational costs and efficiency.
As miners increasingly find themselves in a tighter profit margin scenario, the reliance on transaction fees necessitates a reevaluation of operational strategies. They may have to focus on optimizing their hashing efforts, deploying advanced technologies like AI for predictive maintenance, or potentially diversifying into other cryptocurrencies that might yield better fee structures. The volatility of blockchain fees necessitates prompt adaptation to market conditions to ensure continued revenue flows in a declining hashprice environment.
Managing Risk Amidst Falling Bitcoin Prices
With Bitcoin prices experiencing significant reductions, miners must reassess their risk exposure to maintain their operations. The correlation between Bitcoin’s market price and mining profitability is pervasive; as prices decline, so do the potential revenues from mining. This reality forces miners to implement risk management strategies, ensuring they can endure prolonged periods of lower income. Approaches may include budgeting for operational expenses, augmenting their hash power strategically, or opting for alternative mining contracts that are less sensitive to price fluctuations.
Additionally, miners are exploring longer-term investment strategies to mitigate risks. Whether it’s bolstering infrastructure, forming partnerships, or entering into hedging arrangements, these proactive measures can help sustain operations during downturns. With many miners encountering unprecedented challenges due to the synergy of low hashprice and reduced Bitcoin prices, strategic risk management will be a cornerstone in preserving the future of their mining activities.
Emerging Trends in Bitcoin Mining Strategies
As the Bitcoin landscape evolves, so too do mining strategies in response to economic pressures. Miners are increasingly considering the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) to optimize their operations, from enhancing energy efficiency to predicting market trends. Implementing cutting-edge technology can provide miners with an edge needed to navigate the declininghashprice and maximize profitability despite challenging market conditions. Additionally, the transition to renewable energy sources could offer cost savings that would improve profit margins in a declining revenue environment.
Moreover, resource consolidation is becoming more frequent among miners facing financial strain. In a landscape dotted with volatility, smaller operations may find it increasingly beneficial to merge with larger entities. This consolidation can help reduce costs, pool resources, and share technology advancements, allowing for increased competitiveness against well-capitalized mining farms. The survival of smaller miners may hinge on such strategic collaborations as the market adapts to declining hashprices and evolving profitability challenges.
The Future of Bitcoin Mining: Sustainability and Adaptation
The future of Bitcoin mining hinges on sustainability amidst declining hashprice and profitability challenges. Mining operations must adopt sustainable practices, including energy-efficient hardware, renewable energy sources, and optimized operations. As regulatory scrutiny grows, adapting to green energy sources not only benefits the environment but can also prove to be economically advantageous for miners facing rising energy costs. Sustainability will no longer be just a buzzword — it will become a requisite for survival in the Bitcoin ecosystem.
Additionally, the development of innovative financial instruments, such as futures contracts and pooled mining ventures, may become more pronounced as miners look to stabilize income streams. These innovations will allow miners to better negotiate their exposure to market volatility, especially in a fluctuating environment where hashprice is declining. The future landscape of Bitcoin mining will demand agility, forward-thinking strategies, and a focus on sustainability to ensure continued operation in a rapidly shifting market.
Exploring Alternative Revenue Sources for Miners
In light of the compressed profit margins stemming from falling hashprice, Bitcoin miners are increasingly motivated to explore alternative revenue sources. Diversification is seen as a critical strategy, where miners may turn to services such as staking, liquidity provision, or yielding strategies within decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms. By leveraging their hashing power for varied income generation, miners can insulate themselves from the volatility of exclusively relying on block rewards and transaction fees.
Furthermore, partnerships with emerging DeFi projects can provide miners with new opportunities for revenue streams that align with the evolving landscape of blockchain. This includes utilizing excess computation power for additional applications beyond Bitcoin mining, such as contributing to smart contracts or processing transactions for other blockchain networks. By innovatively leveraging their capabilities and adapting to the market’s needs, miners can enhance their resilience against price fluctuations and revenue declines.
The Impact of Technological Advancements on Mining Efficiency
Technological advancements play a crucial role in the ongoing evolution of Bitcoin mining efficiency. Innovations in hardware, such as application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs), have led to significant improvements in performance and power consumption. Miners now have access to tools that not only increase hashpower but also reduce operational costs, which is paramount in a declining hashprice landscape. More efficient hardware allows miners to remain competitive, even as the market wades through periods of shaky profitability.
In addition to hardware improvements, software also plays an essential part in enhancing mining operations. Automation tools that analyze market trends, performance metrics, and energy consumption can help miners make informed decisions to optimize their operations. Staying ahead of technological advancements is non-negotiable in securing mining success and ensuring operational viability as market conditions shift, particularly with ongoing declines in hashprice.
Navigating the Market Dynamics of Bitcoin Mining
The dynamics of the Bitcoin market are increasingly complex, making it essential for miners to stay attuned to economic fluctuations. Market volatility can create both opportunities and challenging circumstances, particularly when it comes to hashprice and mining profitability. Miners must remain adaptable, ready to pivot when prices drop sharply or when on-chain activity experiences sudden growth. Understanding these market dynamics will empower miners to make nimble decisions to safeguard their operations.
By leveraging market analytics, miners can gain insights into pricing trends, on-chain fee activity, and broader economic indicators affecting Bitcoin’s value. This information is key in creating informed strategies able to withstand the mayhem of market swings. Miners must engage actively with market conditions to carve out pathways for sustained success, ensuring that they can continuously adapt to the surrounding realities of Bitcoin mining amid uncertainty.
Frequently Asked Questions
What factors contribute to the Bitcoin hashprice decline?
The Bitcoin hashprice decline is primarily influenced by the halvings of 2020 and 2024, which cut mining rewards, drastically reducing mining revenue. Additionally, the significant drop in on-chain fees has compounded the situation for miners. As miners receive only about 0.73% of their payouts from transaction fees, the earnings associated with mining profitability have been severely affected.
How does the Bitcoin halving affect mining profitability and hashprice?
Bitcoin halving events reduce the reward miners receive for validating transactions, directly impacting mining profitability. Following the halvings in 2020 and 2024, the current hashprice has declined as miners earn less Bitcoin per petahash, necessitating higher BTC prices or increased on-chain activity to maintain profitability.
What are the implications of reduced blockchain fees on Bitcoin hashprice?
Reduced blockchain fees contribute to the Bitcoin hashprice decline by limiting the potential revenue for miners. With only a small portion of their payouts coming from transaction fees, the overall earnings decrease further when on-chain activities decline, increasing pressure on miners’ profit margins.
What is the significance of the current petahash value in the context of Bitcoin mining?
The current petahash value is critical as it reflects the daily expected revenue generated from one petahash of hashing power. As this value declines, miners face tougher profitability challenges, prompting the need for operational changes or technology upgrades to stay viable in the increasingly harsh Bitcoin mining environment.
Can Bitcoin miners survive the hashprice decline without adjusting their strategies?
Unlikely, as the ongoing hashprice decline leads to tighter profit margins for Bitcoin miners. Without a significant increase in Bitcoin’s price or on-chain activity, miners may be forced to adapt their strategies, such as improving mining technology, consolidating resources, or exploring alternative revenue channels.
How has the Bitcoin price fluctuation impacted mining revenue and hashprice?
The fluctuation in Bitcoin’s price has had a profound impact on mining revenue and hashprice. While Bitcoin experienced an increase in value in November 2025, the hashprice nonetheless declined, indicating that even higher BTC prices are insufficient to offset the revenue losses stemming from declining rewards and fees.
What potential future trends could emerge from the ongoing Bitcoin hashprice decline?
Future trends may include a consolidation of mining operations, increased investment in more efficient mining hardware, or the exploration of AI and alternative revenue streams. Should the hashprice continue to decline, we could see significant changes in the mining landscape and operational approaches as miners adapt to the challenging conditions.
| Key Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Bitcoin Hashprice | $37.48 per PH/s |
| Lowest Record Since | December 2016 |
| Bitcoin Price on April 7, 2025 | $79,874 |
| Bitcoin Price on November 19, 2025 | $91,172 |
| Percentage of Payout from Fees | 0.73% |
| BTC Subsidy per Block | 3.125 BTC |
Summary
The decline in Bitcoin hashprice is indicative of a troubling trend for miners, reflecting a sustained drop in revenues that has reached unprecedented levels. The drastic reduction in hashprice, exacerbated by past halvings and diminished transaction fees, poses a significant challenge to mining profitability. Without substantial increases in Bitcoin’s price or on-chain activity, the future of mining operations is in jeopardy, necessitating innovative strategies or alternative revenue sources to ensure sustainability.