CBDC Uganda is set to revolutionize the financial landscape in the country, marking its entrance into the burgeoning world of central bank digital currencies. This innovative initiative will harness the potential of a tokenized economy Uganda, making financial services more accessible through mobile finance in Uganda. With a collaboration between the Global Settlement Network (GSN) and Diacente Group, the pilot aims to introduce a central bank digital currency backed by treasury bonds, thus opening new channels for economic growth. As Uganda embraces this digital transition, experts predict that it could reshape its digital economy, fostering inclusivity and enhancing investment opportunities. The framework aligns perfectly with national and regional visions for economic transformation and job creation, aiming for significant advancements by 2040.
In the sphere of financial innovation, Uganda is embarking on a groundbreaking journey with its pilot initiative for a central bank digital coin, often referred to in industry circles as a CBDC. This move is indicative of the strides being made towards a modernized financial ecosystem, where mobile finance integrates seamlessly into everyday transactions. The collaboration of prominent entities such as the Global Settlement Network and Diacente Group highlights a significant push towards establishing a token-based economic system that promises wider access to financial tools for the populace. By leveraging treasury bond backing, this pilot aims not only to bring stability to the digital currency landscape but also to foster economic opportunities across sectors like agriculture and energy. With a vision extending to the future, this initiative marks a pivotal step in shaping Uganda’s economic narrative and positioning it within a globally competitive framework.
Transforming the Financial Landscape with CBDC Uganda
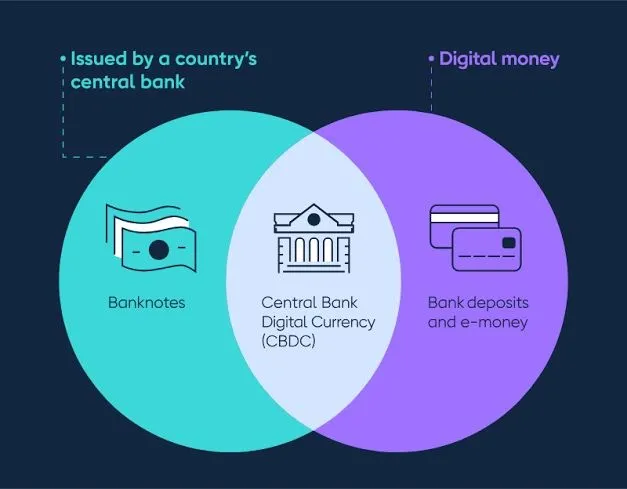
The launch of Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) in Uganda marks a pivotal moment in the country’s financial evolution. With the backing of treasury bonds, the CBDC is designed not just to offer a digital payment method, but also to integrate traditional financial mechanisms with modern technology. This blend of old and new can significantly enhance the security and transparency of transactions, allowing citizens and businesses alike to trust a digital currency that is steeped in a solid financial foundation.
Furthermore, CBDC Uganda aims to leverage mobile finance, which aligns perfectly with the increasing smartphone penetration in the region. By ensuring that this currency is easily accessible via mobile devices, Uganda is set to empower a broader segment of the population, especially those in rural areas who may have limited access to conventional banking services. This digital approach could help bridge the gap between unbanked populations and the financial ecosystem.
Unlocking Potential with a Tokenized Economy in Uganda
The introduction of a $5.5 billion tokenized economy in Uganda positions the nation as a pioneer in Africa’s shift towards digital currencies. By incorporating blockchain technology developed by the Global Settlement Network (GSN) alongside the Diacente Group, Uganda is not merely stepping into uncharted territory; it is constructing a resilient digital infrastructure that could serve as a model for other nations. This initiative will facilitate secure transactions and significantly reduce the cost of doing business, thereby attracting more investment into sectors such as agriculture, mining, and energy.
As the tokenized economy takes root, it will likely lead to enhanced financial inclusion, allowing various sectors to access global capital that was previously out of reach. The potential to tokenize agricultural assets, for instance, could revolutionize how farmers fund their ventures, while also providing a more transparent way to track financial transactions. This is crucial in a country where many contribute to the economy but remain outside the formal financial system.
Mobile Finance in Uganda: The Future is Digital
Mobile finance is rapidly becoming a cornerstone of financial transactions in Uganda, particularly with the rise of mobile phones as essential tools for payments. The integration of CBDC within this mobile ecosystem is anticipated to streamline transactions for everyday users and businesses alike. By leveraging mobile finance, the government can provide a solution that doesn’t require individuals to have bank accounts yet still enables them to participate in the economy digitally.
Additionally, mobile finance encourages innovation in financial products tailored to local needs. As Ugandans become more accustomed to using digital wallets and mobile banking applications, businesses can explore new service delivery models, such as microfinance services or direct-to-consumer payment solutions. This shift towards digital platforms could substantially enhance the country’s digital economy, supporting local entrepreneurs and establishing Uganda as a tech hub in East Africa.
GSN and Diacente Group: Driving Uganda’s Digital Transformation
The partnership between the Global Settlement Network (GSN) and Diacente Group stands out as a significant step towards developing Uganda’s digital infrastructure. Their commitment to launching a tokenized economy not only provides necessary funding but also the technological backbone needed to support a centralized digital currency. This collaboration is critical in creating a robust framework for digital banking and online transactions, which could potentially redefine how financial services are delivered in Uganda.
Moreover, GSN’s expertise in blockchain technology ensures that the infrastructures built are not only secure but scalable, allowing for a transition from pilot projects to a nationwide implementation of digital currency. By establishing this collaborative model, they set a precedent for future initiatives in the region and inspire confidence among stakeholders and investors looking to engage in Uganda’s burgeoning digital marketplace.
Aligning with Uganda’s Vision 2040 and Agenda 2063
The pilot of a CBDC in Uganda is in line with national objectives outlined in Vision 2040 and the African Union’s Agenda 2063. Both frameworks aim to foster economic growth and development through innovation, sustainable practices, and inclusivity. By adopting a digital currency backed by tangible assets and focused on mobile accessibility, Uganda is positioning itself strongly on the path to achieving these ambitious goals.
As the nation embraces these progressive strategies, the CBDC initiative is expected to contribute significantly to job creation and the export economy. With an estimated one million jobs to be generated, this move will not only enhance individual livelihoods but also stimulate overall economic activity. The partnership’s forward-thinking approach aligns with regional aspirations for a united and prosperous Africa, driving home the importance of digital transformation in realizing these visions.
The Role of Regulatory Compliance in CBDC Implementation
Implementing a CBDC in Uganda involves a careful navigation of regulatory landscapes to ensure that the digital currency operates within the framework of existing financial laws. Regulatory compliance will be paramount in maintaining user trust and fostering an ecosystem where innovation can thrive without compromising security. GSN and Diacente Group’s collaboration will likely focus on establishing robust compliance protocols that cater to the specifics of Uganda’s evolving financial ecosystem.
Additionally, engaging with stakeholders—including government entities, financial institutions, and the public—will be crucial in shaping the regulatory guidelines that govern the use of CBDC. Ensuring transparency throughout this process can help alleviate any concerns about privacy and security among potential users. By prioritizing regulatory compliance, Uganda can pave the way for a seamless transition to digital financial solutions, further solidifying its position as a leader in the African digital economy.
Economic Impact of CBDC on Local Businesses in Uganda
The implementation of CBDC in Uganda is expected to have a transformative impact on local businesses by enhancing payment processes and reducing transaction costs. With the ability to transact in a digital currency, businesses can benefit from faster settlements and lower fees associated with traditional banking methods. This upsurge in operational efficiency could drive profitability and competitiveness among local enterprises, particularly in sectors like agriculture and trade.
As businesses adapt to this digital scheme, there is also potential for innovation in how goods and services are exchanged, fostering a more dynamic marketplace. Additionally, as financial literacy improves alongside the adoption of digital currencies, local entrepreneurs may discover new opportunities that were previously unattainable. The ripple effects of adopting CBDC will likely create an environment conducive to growth and sustainability for the local economy.
Challenges and Opportunities for CBDC in Uganda
While the prospects for CBDC in Uganda are promising, several challenges must be addressed for successful implementation. These may include technological infrastructure, cybersecurity risks, and public acceptance of digital currencies. Educating the public about the benefits and uses of CBDC will be vital to overcoming skepticism and ensuring widespread adoption. Moreover, creating a resilient technological foundation capable of supporting millions of transactions safely is paramount to the initiative’s success.
However, these challenges also present unique opportunities for innovation and collaboration. By engaging with tech companies, financial institutions, and educational organizations, Uganda can cultivate an ecosystem that supports not just the CBDC roll-out but also broader advancements in the digital economy. As stakeholders work together to address these hurdles, they can lay the groundwork for a vibrant and inclusive financial landscape that benefits all Ugandans.
Future Prospects of CBDC in the Global Economy
As countries worldwide explore the concept of Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs), Uganda’s initiative can serve as a case study for other emerging economies. By effectively integrating CBDC into its financial framework, Uganda can offer insights into the benefits and challenges of digital currencies. This experience will be invaluable for global discussions on the role of CBDCs in stimulating economic growth, financial inclusion, and resilience against economic shocks.
In the long term, Uganda has the potential to emerge as a leader in the adoption of digital currencies, influencing regional policies and financial practices across Africa. As neighboring countries observe Uganda’s progress, they may seek to emulate its approach to digital finance, contributing to a more unified and streamlined financial infrastructure on the continent. This could change the global perception of Africa, showcasing it as a frontier for financial innovation and digital economic development.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is CBDC Uganda and how will it be implemented?
CBDC Uganda refers to the country’s initiative to introduce a central bank digital currency, which will be piloted using GSN’s blockchain technology. This digital currency is designed to be backed by treasury bonds and will facilitate access through mobile devices, driving innovation in Uganda’s digital economy.
How will the central bank digital currency impact mobile finance in Uganda?
The introduction of CBDC Uganda is expected to revolutionize mobile finance by providing secure, efficient, and accessible financial services. By integrating with existing mobile platforms, this initiative will enhance transactional capabilities and financial inclusion across various sectors.
What are the benefits of the tokenized economy in Uganda as proposed by GSN and Diacente Group?
The tokenized economy in Uganda, valued at $5.5 billion, aims to attract global capital by digitizing sectors such as agriculture and energy. CBDC Uganda will therefore enable better management of real-world assets, promote regulatory compliance, and unlock economic opportunities for local populations.
What role does Uganda’s Vision 2040 play in the CBDC Uganda initiative?
Uganda’s Vision 2040 emphasizes economic transformation and innovation, which aligns closely with the goals of CBDC Uganda. By adopting a central bank digital currency, Uganda aims to enhance its digital economy, drive job creation, and increase exports as part of its long-term development strategy.
How is GSN’s blockchain technology relevant to the CBDC initiative in Uganda?
GSN’s blockchain technology is crucial for CBDC Uganda as it underpins the secure transaction processes and supports the development of a transparent digital economy. This technology enables efficient financial operations and can integrate with Uganda’s existing financial infrastructure.
What sectors will benefit from the CBDC Uganda pilot project?
The CBDC Uganda pilot project aims to digitize key sectors including agriculture, mining, and energy. By backing the currency with treasury bonds and facilitating mobile access, it will create a more efficient and accessible economic environment.
What are the expected outcomes of piloting CBDC in Uganda?
The expected outcomes of piloting CBDC Uganda include the creation of over one million jobs, the facilitation of $10 billion in annual exports, and the strengthening of Uganda’s financial infrastructure. This pilot aligns with broader goals like the African Union’s Agenda 2063.
How will CBDC Uganda promote inclusive growth?
CBDC Uganda is designed to promote inclusive growth by providing accessible financial tools via mobile devices, enabling wider participation in the economy. By offering a central bank digital currency, it helps to integrate marginalized communities into the financial system.
What is the significance of the partnership between GSN and Diacente Group for Uganda’s digital economy?
The partnership between GSN and Diacente Group is significant for Uganda’s digital economy as it brings together resources and expertise to launch CBDC Uganda. This collaboration is pivotal in establishing a tokenized economy that aims for sustainable development and financial innovation.
What challenges might arise during the implementation of CBDC Uganda?
Challenges in implementing CBDC Uganda might include ensuring cybersecurity, navigating regulatory frameworks, and achieving high levels of public trust and digital literacy among users. Addressing these issues will be vital for the success of this central bank digital currency.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Launching CBDC | Testing Uganda’s first central bank digital currency, backed by treasury bonds. |
| Partnership | Collaboration between the Global Settlement Network and Diacente Group. |
| Investment | $5.5 billion tokenized economy project in the Karamoja region. |
| Technology Used | Utilization of blockchain technology to enhance sector digitization. |
| Goals | Focus on agriculture, mining, and energy sectors to unlock global capital. |
| Economic Impact | Projected creation of over 1 million jobs and $10 billion in annual exports. |
| Alignment with Policies | Supports Uganda’s Vision 2040 and the African Union’s Agenda 2063. |
Summary
CBDC Uganda marks a significant stride toward financial innovation, focusing on leveraging a central bank digital currency that is bolstered by treasury bonds. This initiative not only aims to modernize Uganda’s financial landscape but also seeks to integrate mobile access for widespread usage. By fostering a tokenized economy in Karamoja, the project promises to enhance investment in key sectors and create a substantial economic impact, including job creation and increased exports. Overall, CBDC Uganda represents a transformative approach to achieving inclusive growth in line with national and continental aspirations.