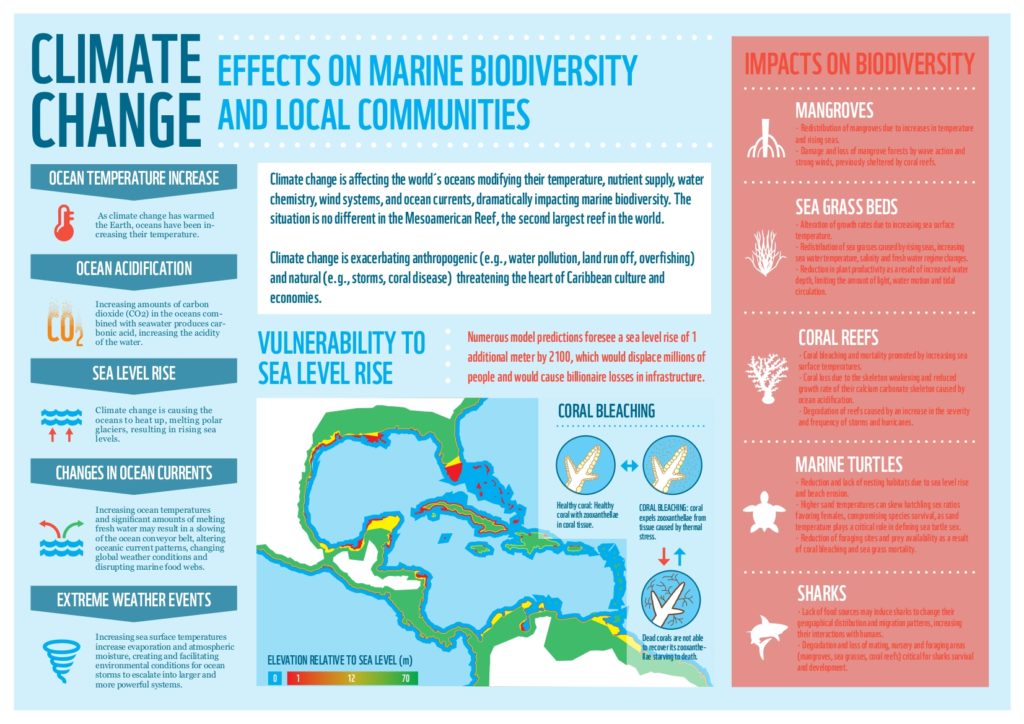
The impact of climate change on marine biodiversity is a critical issue that demands urgent attention. As our planet warms, marine ecosystems face unprecedented challenges, from rising sea temperatures to ocean acidification. These changes are not only threatening the delicate balance of marine life but also jeopardizing the livelihoods of millions who depend on healthy oceans. Coral reef decline, a direct consequence of warmer waters, exemplifies the crisis, as these vibrant systems host an array of marine species. Furthermore, species distribution shifts are occurring as aquatic organisms migrate in search of cooler habitats, highlighting the urgent need to understand and address the climate change effects on oceans.
The repercussions of global warming on ocean life are alarming and multifaceted. With a significant rise in temperatures, marine environments are experiencing shifts that impact both marine ecosystems and human activities. Increased acidity in seawater affects vital species that form the backbone of marine food webs, leading to concerns over species viability and commercial fisheries. Furthermore, the deterioration of coral systems signifies broader ecological changes that could lead to a loss of biodiversity. It’s crucial to explore sustainable solutions and adaptive strategies to support the resilience of ocean habitats amid these environmental challenges.
The Effects of Climate Change on Marine Biodiversity
Climate change has profound and multifaceted effects on marine biodiversity, driving a range of ecological changes that threaten marine life. Rising sea temperatures are causing significant shifts in species distributions, with many fish and marine mammal populations moving toward cooler waters. This not only endangers the habitats of many species but also complicates local fishing practices, affecting livelihoods and the sustainability of fisheries. Furthermore, coral reefs, which support an estimated 25% of all marine species, are particularly affected by these changes, suffering from increased bleaching events and declining health.
In addition to rising temperatures, ocean acidification is an emerging concern that compounds the impacts of climate change on marine biodiversity. Increased levels of CO2 in the atmosphere are leading to higher absorption of carbon dioxide by the oceans, causing a decrease in pH levels. This acidification can have catastrophic effects on calcifying organisms, such as mollusks and corals, which struggle to maintain their shells and skeletons in more acidic conditions. The decline of these foundational species can have cascading effects throughout the marine food web, ultimately disrupting entire ecosystems.
Understanding Ocean Acidification and Its Impact on Marine Life
Ocean acidification refers to the ongoing decrease in the pH of the Earth’s oceans, primarily driven by the increasing atmospheric CO2 from human activities. As the oceans absorb more carbon dioxide, the chemical balance is disrupted, leading to a more acidic environment that adversely affects marine organisms. Species that rely on calcium carbonate to form their shells, such as oysters, clams, and some plankton, face significant challenges as acidic waters hinder their ability to grow and survive. This disruption in the base of the marine food web can lead to declines in fish populations that depend on these organisms for food, ultimately affecting marine biodiversity.
Moreover, the consequences of ocean acidification extend beyond just individual species—it can alter entire ecosystems. Coral reefs, known for their incredible biodiversity, are especially at risk as they struggle to maintain their structural integrity in acidic waters. Healthy coral reefs provide essential habitats for countless marine species, and their decline means that many of these organisms lose their homes. As aquatic biodiversity diminishes, the resilience of marine ecosystems is compromised, making them less capable of adapting to other stressors such as overfishing and pollution.
The Consequences of Coral Reef Decline
Coral reefs face substantial threats from climate change, primarily due to rising sea temperatures leading to increased bleaching events. When corals expel the symbiotic algae (zooxanthellae) that give them color and provide energy, they become more susceptible to disease and mortality. This bleaching phenomenon not only diminishes the reefs’ ecological function but also affects the myriad of organisms that rely on reefs for food and shelter. The loss of these biodiversity hotspots ripples through the marine ecosystem, resulting in diminished fish populations and increased competition for remaining resources.
In addition, the physical structure of coral reefs serves as a natural barrier against storms and coastal erosion. Their decline compromises protective ecosystems, accelerating shoreline erosion and increasing vulnerability to extreme weather events. The ramifications are significant not only for marine life but also for coastal communities that depend on healthy reefs for tourism, fishing, and protection from storms. Therefore, addressing the decline of coral reefs is crucial not just for biodiversity but also for the socio-economic stability of communities worldwide.
Shifts in Species Distribution Due to Climate Change
The ongoing shifts in species distribution as a response to climate change are increasingly evident in marine environments. As ocean temperatures rise, many fish and marine species are moving towards higher latitudes or deeper waters in search of suitable habitats. This redistribution alters ecosystem dynamics, affecting predator-prey relationships and leading to increased competition among species. For instance, traditional fishing grounds may become less productive as target species migrate, impacting local economies and food security.
Moreover, these shifts can lead to the introduction of non-native species into new areas, further destabilizing existing ecosystems. Invasive species can outcompete native organisms for resources, disrupt established ecological balances, and lead to further declines in biodiversity. The complexities of these shifts underscore the need for adaptive management strategies in fisheries and conservation efforts to mitigate the adverse effects of climate change on marine biodiversity.
Conservation Efforts to Address Climate Change Impacts
In response to the escalating threats posed by climate change, concerted conservation efforts are being initiated worldwide. Marine Protected Areas (MPAs) are one effective strategy employed to safeguard vital habitats and promote the resilience of marine biodiversity. By restricting certain activities, such as fishing and coastal development, MPAs provide a refuge for marine species, allowing ecosystems the opportunity to recover and adapt to changing conditions. The establishment and enforcement of these areas are pivotal in ensuring that marine biodiversity is preserved for future generations.
Furthermore, initiatives aimed at restoring damaged ecosystems, such as coral reef restoration projects, are gaining momentum. These projects often involve replanting corals and enhancing habitat structures to support diverse marine life. Additionally, reducing pollution and implementing sustainable fishing practices are essential components of any comprehensive strategy to combat climate change effects on oceans. Promoting awareness and fostering global cooperation are also vital in ensuring the success of these conservation efforts, as the health of marine biodiversity is intrinsically linked to the overall health of our planet.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does climate change affect marine biodiversity?
Climate change severely impacts marine biodiversity through rising sea temperatures, causing coral bleaching and altering species distributions. Warmer oceans force marine species to migrate to cooler waters, disrupting local ecosystems and fishing practices.
What role does ocean acidification play in the decline of marine biodiversity?
Ocean acidification, a direct result of increased CO2 emissions, adversely affects species like mollusks and crustaceans, which need calcium carbonate for their shells. This disrupts marine food webs and threatens commercial fisheries, further diminishing marine biodiversity.
What are the impacts of coral reef decline on marine biodiversity?
Coral reefs are vital for marine biodiversity as they provide habitat for a multitude of species. The decline of coral reefs due to climate change leads to habitat loss, decreased species richness, and potential ecosystem collapse, ultimately affecting marine food security.
How are species distribution shifts related to climate change effects on oceans?
Species distribution shifts occur as marine organisms move to cooler waters or deeper depths in response to rising ocean temperatures. This phenomenon disrupts existing ecological relationships, as predators and prey may shift at different rates, complicating conservation efforts.
What conservation strategies are effective against the impacts of climate change on marine biodiversity?
Effective conservation strategies include establishing marine protected areas (MPAs), restoring coral reefs, and implementing measures to reduce pollution. These strategies aim to protect marine environments from the detrimental effects of climate change and support the resilience of marine biodiversity.
| Key Point | Description |
|---|---|
| Rising Sea Temperatures | Increasing ocean temperatures lead to coral bleaching and shifting marine species distributions. |
| Ocean Acidification | Higher CO2 levels create more acidic oceans, affecting shell-based species and disrupting food webs. |
| Impact on Coral Reefs | Coral reefs are vital for marine biodiversity but are declining due to bleaching events. |
| Shifts in Species Distribution | Species are migrating towards cooler waters, impacting ecosystems and food chains. |
| Conservation Efforts | Efforts include protecting marine areas, restoring reefs, and reducing pollution. |
Summary
The impact of climate change on marine biodiversity is profound and multifaceted. As ocean temperatures rise and acidification intensifies, the delicate balance of marine ecosystems is threatened, with coral reefs and various marine species facing dire consequences. Immediate and collaborative global action is essential to mitigate these effects, ensuring the protection of marine life and the health of ocean ecosystems for future generations.