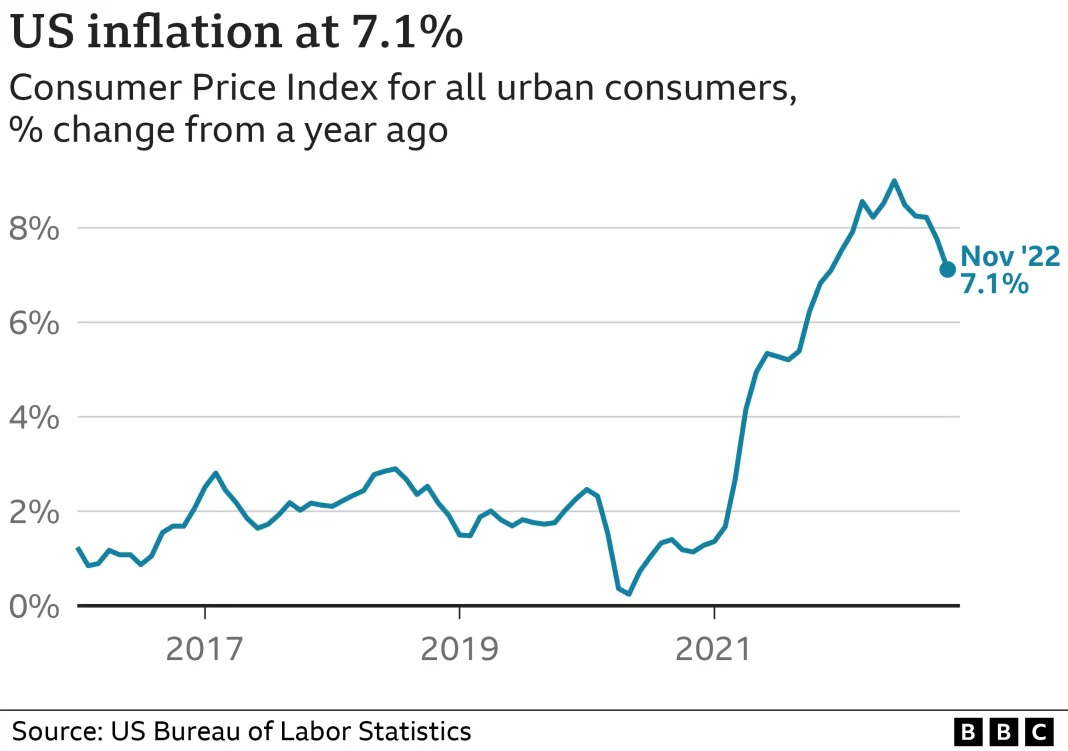
The U.S. inflation report released by the Bureau of Labor Statistics has drawn considerable attention, revealing a notable increase in the Consumer Price Index (CPI) for September. The report indicated a 0.3% rise, driven by significant jumps in gas and food prices, underscoring the persistent inflationary pressures facing the economy. As inflation data for September shows CPI reaching 3%, analysts are keenly observing the implications for Federal Reserve interest rates and possible changes in monetary policy. Factors such as tariffs have also emerged as significant contributors to this CPI increase, influencing consumer behavior and overall market sentiment. With these insights, stakeholders are left to ponder how these developments may shape economic conditions in the coming months.
Analyzing the recent report on inflation within the United States reveals critical trends in the economy that could impact consumers and policymakers alike. The latest figures indicate a noteworthy uptick in the Consumer Price Index, showcasing a 0.3% rise in September, largely fueled by hikes in energy and food prices. Such inflation indicators are essential for adjusting fiscal strategies, especially as the Federal Reserve considers interest rates in response to shifting economic signals. Additionally, external factors, like tariffs and their cascading effects on pricing, are weighing heavily on analysts’ minds as they decipher the complexities of rising costs. This landscape of inflationary data not only highlights immediate concerns but also prompts discussions about future financial stability.
Understanding the Latest U.S. Inflation Report
The recent U.S. inflation report published by the Bureau of Labor Statistics revealed notable insights into the state of the economy, particularly the Consumer Price Index (CPI), which increased by 0.3% in September. This figure, while indicating a rise in prices, was less than the anticipated 0.4% and has compelling implications for consumers. A key driver of this increase was the sharp rise in gas prices, which surged by 4.1%, reflecting ongoing volatility in energy markets. Food prices also contributed, with an increase of 0.2%, underscoring the persistent pressures faced by American households.
Analysts have pointed to a combination of factors influencing these inflationary trends, including tariffs that were introduced in recent years. Tariffs on various goods have led to increased costs that are now being passed onto consumers. The interplay between tariffs, rising commodity prices, and overall consumer spending has made the CPI a critical piece of data for economists and policymakers alike. Understanding the nuances of this inflation report is crucial as it directly impacts Federal Reserve strategies on interest rates and potential economic forecasts.
The Impact of Tariffs on Inflation Data for September
Tariffs have emerged as one of the significant contributors to the inflation data reported in September. As the U.S. government implemented various tariff policies to curb trade deficits, the resulting increases in import costs have trickled down to everyday expenses for consumers. Economists, including Heather Long, have emphasized that tariff costs have compounded inflation, particularly evident in sectors sensitive to price fluctuations, such as food and energy. This highlights a growing concern among consumers who are grappling with heightened living costs as their purchasing power is diminished.
In examining the implications of tariffs on the overall inflation picture, it becomes clear that these trade policies may not only affect immediate pricing but can also have long-term repercussions on the economy. Retailers and manufacturers may be forced to adjust their pricing strategies to account for expected cost increases, thereby perpetuating a cycle of inflation. Policymakers, especially those at the Federal Reserve, will have to navigate these challenges carefully, as they weigh the need to support economic growth against the persistent inflationary pressures heightened by tariffs.
Market Reactions and Federal Reserve Interest Rate Policies
Following the release of the inflation report, stock markets exhibited a positive response, with S&P 500 futures climbing by 1%, reflecting investor sentiment in light of the economic data. This reaction might appear counterintuitive given rising inflation; however, market participants often interpret softer-than-expected inflation data as a sign that the Federal Reserve may be inclined to keep interest rates lower for longer. This scenario creates an environment where stocks can thrive, reducing the cost of borrowing and encouraging investment.
The Federal Reserve is closely monitoring the CPI and other economic indicators as they shape their interest rate policies. With inflation currently exceeding the Fed’s 2% target yet showing signs of moderation, there is a growing belief that the central bank might consider further reductions in interest rates. This focus on balancing inflation control with economic growth is critical, as the Fed must consider the potential impact on employment and consumer confidence moving forward. As Art Hogan mentioned, the ongoing assessment of labor market conditions will play a pivotal role in the Fed’s decision-making process, factoring into the broader strategy designed to maintain economic stability.
Consumer Price Index Trends and Economic Outlook
The Consumer Price Index (CPI) has shown an increasing trend that raises concerns about the cost of living for Americans. With the CPI reaching a significant 3% increase over the past year, analysts are wary of further price escalation, resulting in increased scrutiny of both consumer habits and economic policies. Consumers are feeling the pressure both at the gas pump and in grocery stores, translating to a heightened cost of living that is not only squeezing household budgets but also impacting discretionary spending.
Moving forward, the economic outlook will largely depend on how these inflation trends influence consumer behavior and business investment decisions. Companies might adjust their pricing structures in response to increased operational costs stemming from inflationary pressures, which can further exacerbate the cycle. Should inflation become entrenched, it could present challenges for the Federal Reserve in achieving its dual mandate of price stability and full employment, necessitating a careful approach to interest rate adjustments and fiscal policy responses.
Potential Consequences of Inflation on Consumer Behavior
Inflation, particularly as indicated by the recent CPI increase, has potential consequences for consumer behavior. As prices rise, individuals may start prioritizing essential goods over discretionary spending, leading to shifts in market demand. Increased costs of goods and services can create a sense of urgency among consumers to adjust their financial habits, opting for budget-friendly alternatives or delaying purchases altogether. This transformation in consumer behavior can ripple throughout the economy, influencing business revenue patterns and growth trajectories.
Moreover, the psychological effects of inflation can alter consumers’ expectations about future pricing, leading to a phenomenon known as “price anchoring.” As individuals become accustomed to higher prices, they may internalize these changes, making them more resistant to future price decreases. Businesses, on their end, might respond to expected shifts in consumer demand by adjusting their supply chains and pricing strategies, creating a feedback loop that perpetuates inflationary pressures over time.
Federal Reserve’s Response to Rising Inflation Rates
In the face of rising inflation rates, the Federal Reserve is tasked with determining its response strategy amidst changing economic indicators. The latest CPI report showing a 3% increase calls for the Fed to assess whether to adjust interest rates to combat inflation while supporting economic growth. Central banks traditionally employ interest rate adjustments as a tool to manage inflation – raising rates to dampen spending or lowering them to stimulate the economy. With inflation sitting above its target, the Fed faces a crucial decision point.
Economists note that the Fed may adopt a careful approach in responding to rising inflation given the importance of supporting labor markets. Balancing the need to manage inflation without hindering economic recovery is paramount. The statements from market strategists like Art Hogan underscore the Fed’s focus on labor data, which may suggest that while inflation requires attention, employment levels take precedence in determining monetary policy. The delicate dance between tackling inflation and fostering a supportive economic environment will determine the Fed’s path moving forward.
Role of Energy Prices in Current Inflation Dynamics
Energy prices have played a pivotal role in shaping the current inflation dynamics reflected in the September CPI report. Gasoline prices surged by 4.1%, significantly influencing the overall increase in the CPI. Fluctuations in energy prices can stem from a variety of factors including geopolitical tensions, changes in supply and demand, and seasonal variations. As energy remains a fundamental component of the consumer expense basket, changes in this category often have far-reaching implications for overall inflation trends.
Furthermore, understanding the volatility of energy markets is crucial for economists forecasting future inflation numbers. As consumers continue to feel the impact of rising energy costs, it may lead to broader economic ramifications, influencing consumer confidence and spending behavior. Policymakers must account for these factors as they construct strategies to mitigate inflationary pressures, emphasizing the need for energy stability in inflation control efforts.
CPI and Employment: A Complex Relationship
The relationship between the Consumer Price Index (CPI) and employment figures is complex yet critical in informing economic policy. While the CPI indicates rising prices, employment data sheds light on economic health and workforce stability. The Federal Reserve uses both metrics to craft appropriate monetary policies. High inflation combined with high unemployment presents a challenging scenario; thus, understanding this relationship is vital for optimizing policy responses. Historically, periods of rising prices can lead to increased labor market participation as workers seek higher wages to keep pace with inflation.
However, in a more nuanced perspective, the Fed must differentiate between transitory inflation spurred by external factors – such as tariffs or energy price spikes – and persistent inflation indicative of structural economic issues. As the Fed contemplates interest rate adjustments, it does so with the knowledge that employment stability can help buffer against the negative impacts of inflation, leading to enhanced consumer confidence and spending. Therefore, fostering a resilient labor market remains an essential goal amidst rising CPI numbers.
Future Directions: Monitoring Inflation and Economic Indicators
Moving forward, close monitoring of inflation data and other economic indicators will be critical to understanding the trajectory of the U.S. economy. The September CPI report serves as a benchmark for policymakers, illuminating the need for responsive strategies to ensure economic stability. Inflation can directly influence Federal Reserve decisions regarding monetary policy, leading to possible adjustments in interest rates designed to foster sustainable growth.
Periodic updates on the CPI and other relevant financial metrics will guide market expectations and business planning. As employers anticipate shifts in consumer purchasing patterns due to inflation, it is essential for both businesses and policymakers to adopt proactive strategies. Continuous evaluation of these indicators will help forge a path toward economic resilience, providing clarity amid the uncertainties posed by inflation and associated economic dynamics.
Frequently Asked Questions
What key insights does the latest U.S. inflation report provide about the Consumer Price Index (CPI)?
The latest U.S. inflation report from the Bureau of Labor Statistics reveals that the Consumer Price Index (CPI) increased by 0.3% in September, primarily driven by significant rises in gasoline prices (4.1%) and modest increases in food prices (0.2%). This marks a notable trend as inflation data indicates a steady rise in living costs.
Why did analysts find the CPI increase of 0.3% in September lower than expected?
Analysts had anticipated a CPI increase of 0.4% for September, making the reported 0.3% rise lower than expectations. This was surprising, especially given the rising gas and food prices contributing to overall inflation data.
What role do tariffs play in the context of the U.S. inflation report?
The U.S. inflation report indicated that tariffs are a significant contributor to rising prices, particularly in gasoline and food sectors. Analysts, including Heather Long, emphasize that tariffs enacted during the last administration have led to increased costs for consumers.
How does the CPI increase impact Federal Reserve interest rate decisions?
With the CPI reaching 3%, the Federal Reserve may continue to focus on easing interest rates rather than solely reacting to inflation numbers. Given the softening labor market data, there are indications that the Fed might consider lowering rates to stimulate the economy.
What are the implications of the inflation data for the average American consumer?
The inflation data, particularly the CPI increase of 3%, suggests that consumers are experiencing a consistent rise in the cost of living. This development can strain household budgets, especially due to the rising costs of essential items such as food and gas.
How has the stock market reacted to the latest U.S. inflation report?
The stock market showed a positive reaction to the inflation report, with S&P 500 futures rising by 1%, reaching record highs. Investors seem encouraged by the slower-than-expected inflation, suggesting confidence in ongoing economic policies.
What does the September inflation report imply about future CPI trends?
The September inflation report indicates that while inflation is rising, recent data suggests a potential stabilization in the rate of increase. Analysts are closely monitoring these trends as they could predict future CPI movements and their impact on economic policy.
How might the Federal Reserve’s stance on interest rates evolve following the September inflation report?
Following the September inflation report, the Federal Reserve may prioritize adjusting interest rates based on labor market indicators rather than solely on CPI fluctuations. This suggests a more dovish approach to monetary policy amidst uncertain inflation trends.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| CPI Increase | The CPI rose by 0.3% in September. |
| Main Contributors | Increases in gasoline (4.1%) and food prices (0.2%) were the main contributors. |
| Significance of 3% CPI | It’s the first time CPI has reached this level since January, indicating rising living costs for Americans. |
| Market Reaction | S&P 500 futures climbed 1%, indicating positive investor sentiment despite inflation. |
| Federal Reserve’s Response | The Fed may continue to lower interest rates, focusing on labor market data more than rising inflation. |
Summary
The U.S. inflation report released by the Bureau of Labor Statistics reveals an important increase in the Consumer Price Index, which rose by 0.3% in September. This uptick was primarily driven by rising prices in gas and food, marking a significant moment as the CPI reached 3%, the highest since January. As inflation continues to affect living costs, the Federal Reserve is expected to respond by potentially lowering interest rates, prioritizing labor market conditions over mere inflation metrics. This dynamic encapsulates the ongoing economic challenges and market reactions, providing crucial insights for investors and policymakers alike.