Web scraping is an essential technique in data extraction that allows users to systematically collect information from websites. By utilizing specialized web scraping tools, businesses can automate data retrieval to gain insights into market trends, competitor activities, and consumer behavior. Understanding how web scraping works starts with sending a request to web servers, then parsing the HTML response to extract valuable data efficiently. This technique can be applied across various industries, demonstrating its versatility through applications in market research, news aggregation, and real estate analysis. Emphasizing ethical web scraping practices is crucial to ensure compliance with legal standards while leveraging powerful data extraction techniques.
Data harvesting from online sources, commonly referred to as web scraping, encompasses an array of methodologies that enhance information retrieval from the vast landscape of the internet. Known for its utility in fields like digital marketing and research, web scraping enables analysts to compile and assess vast quantities of data seamlessly. Techniques for data extraction, including HTML parsing and structured storage, facilitate this process, allowing users to uncover hidden insights. By exploring alternative phrases like web data gathering or online content scraping, we can appreciate the significance of these practices in conducting thorough analyses across various platforms. The focus on responsible scraping practices is essential, ensuring that data collection aligns with ethical guidelines and web compliance.
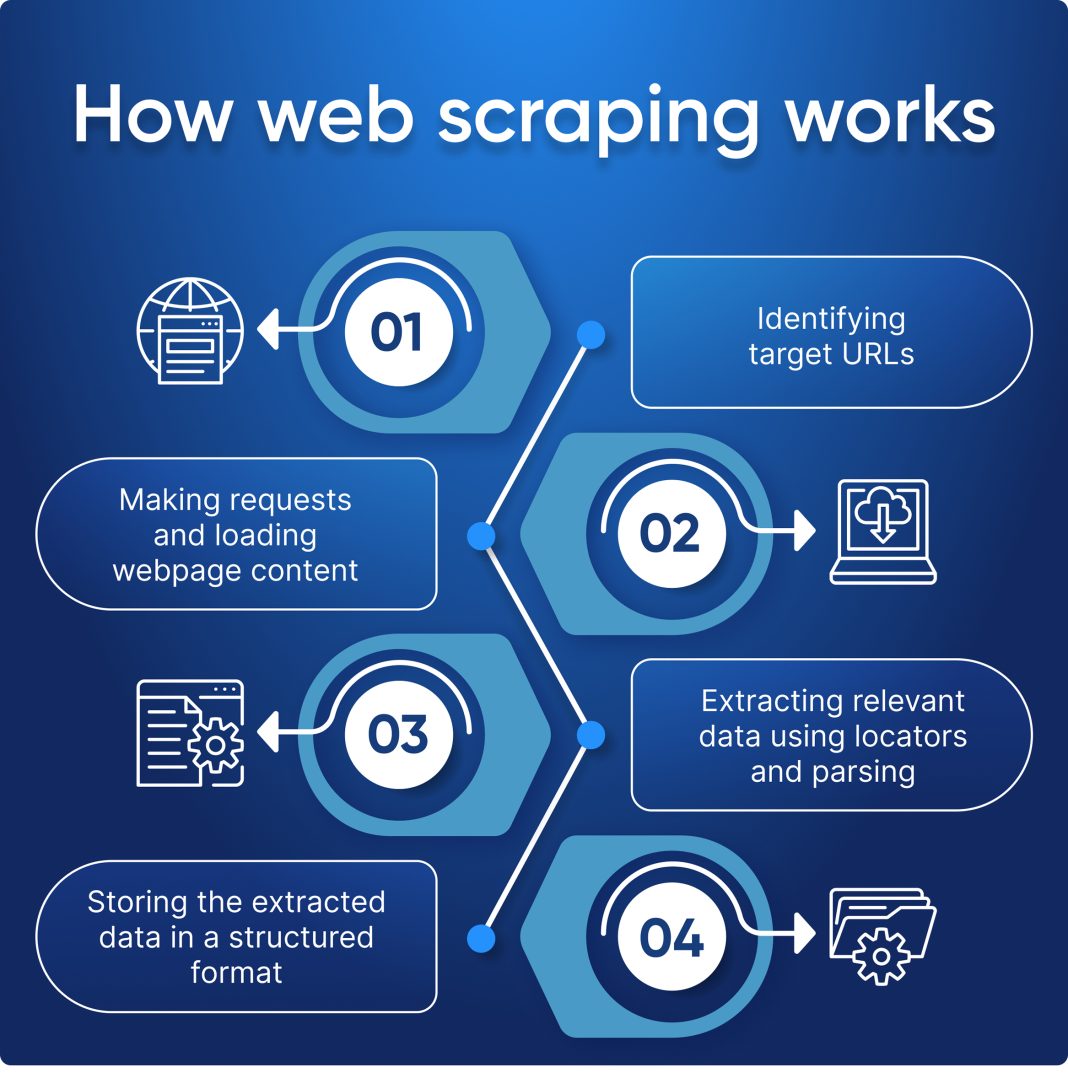
Understanding How Web Scraping Works
Web scraping operates through a systematic approach that involves multiple steps, making it essential for anyone looking to harness data from the internet. First, the process begins with sending a request to the target server using HTTP protocols. This request is crafted in a manner that is recognized by the server, which then retrieves the relevant data associated with the requested webpage. The efficacy of web scraping hinges on the ability to manipulate these requests correctly and understand server responses.
Once the scraping tool successfully receives the server’s response, it downloads the HTML content of the webpage. The next critical phase involves parsing this HTML using specialized tools like BeautifulSoup or Scrapy, which convert the raw data into a navigable format. Scrapers need to identify specific tags, classes, or IDs to extract meaningful data. This structured approach ensures that web scraping is not just about obtaining information but also about curating it effectively for analysis.
Web Scraping Applications Across Industries
The versatility of web scraping makes it an invaluable tool across various sectors. For instance, in market research, companies utilize web scraping techniques to gather competitive intelligence including product pricing, consumer sentiment, and market trends. By systematically aggregating data from multiple sources, businesses can gain insights that drive their strategy and operational decisions, thus enhancing their market positioning.
Similarly, in the realm of news aggregation, web scraping helps numerous platforms pull articles from various news sites, allowing users to access a diverse range of stories in one place. For example, by scraping data from websites, these aggregators can compare headlines, analyze media coverage trends, and provide personalized news feeds based on scraped content. This functionality enriches the user experience and showcases the incredible benefits of integrating web scraping into digital ecosystems.
Ethical Considerations in Web Scraping
As the practice of web scraping continues to evolve, ethical considerations have become paramount. Engaging in web scraping without full understanding of a website’s terms of service or the legal boundaries can lead to significant repercussions. Scrapers must always adhere to the guidelines set by a site’s `robots.txt` file, which indicates where scraping is permitted or prohibited. Respecting these protocols not only fosters responsible use but also strengthens relationships between data collectors and website owners.
Moreover, ethical web scraping goes beyond legality; it encompasses the importance of using data responsibly. This means avoiding excessive request rates that could overwhelm a server, undermining its performance for regular users. By implementing intelligent scraping strategies that incorporate rate limiting and thoughtful data storage methods, scrapers can ensure they collect data while maintaining respect for the source. This balance is vital in cultivating an ethical landscape as web scraping practices continue to grow.
Popular Web Scraping Tools and Frameworks
Selecting the right tools for web scraping is crucial to streamline the data extraction process efficiently. While there are numerous options available, some of the most popular tools include BeautifulSoup, Scrapy, and Selenium. BeautifulSoup is revered for its simplicity and ease of use, which makes it a suitable choice for beginners who are exploring the realm of web scraping. Scrapy, on the other hand, is a full-fledged framework that handles synchronous requests and provides built-in support for complex scraping scenarios, making it favored among seasoned developers.
For dynamic and JavaScript-heavy websites, Selenium serves as a critical tool since it allows for browser automation which can simulate user interactions. Selecting the appropriate scraping tool depends largely on the specific needs of your project, including the complexity of the site being targeted and the volume of data to be handled. By leveraging these tools effectively, one can maximize the benefits of web scraping and achieve a robust data acquisition strategy.
Data Extraction Techniques in Web Scraping
Data extraction techniques are fundamental to the success of web scraping endeavors. The most common method involves parsing the HTML structure of a webpage to identify relevant data fields, such as product descriptions, prices, and user reviews. Techniques can vary based on the type of data being extracted; for instance, XPath and CSS selectors allow scrapers to directly target specific elements, thus simplifying the extraction process.
In addition to standard techniques, advanced data extraction might involve processing websites that use API endpoints or implementing machine learning models to interpret unstructured data. These sophisticated techniques enhance the scraper’s ability to collect extensive datasets while overcoming challenges such as CAPTCHA and anti-scraping measures. By refining these data extraction methods, businesses can streamline their operations and uncover rich insights from web data.
Legal Implications of Web Scraping
Legal implications play a crucial role in the practice of web scraping, making it essential for organizations to understand the boundaries within which they operate. Many websites have specific terms of service that dictate whether scraping is permissible, and violating these can lead to legal challenges. Additionally, the interpretation of laws such as the Computer Fraud and Abuse Act (CFAA) can vary, leading to potential legal ramifications for scrapers who do not proceed with caution.
Moreover, compliance with data protection regulations such as GDPR further complicates the landscape of web scraping. Scrapers need to be sensitive to personal data considerations, ensuring that they do not infringe on individuals’ rights. By understanding these legal nuances and establishing a strong compliance framework, companies can engage in web scraping responsibly, protecting not only themselves but also the privacy rights of users.
Maximizing Efficiency in Data Collection
To maximize efficiency in data collection, web scraping strategies should focus on optimization techniques that improve speed and reduce errors. Implementing asynchronous requests can dramatically enhance the speed of data gathering, as multiple requests can be sent simultaneously without the need to wait for a single response. Additionally, using proxies can prevent IP bans by distributing requests across various addresses, thereby ensuring continual access to target websites.
Moreover, maintaining an adaptable scraping logic is vital, as web scraping often entails dealing with dynamic content. Incorporating robust error handling and making use of data validation methods during the extraction phase can help ensure data integrity. For teams engaged in large-scale scraping operations, automating these processes with scheduled scripts can provide timely insights while conserving resources.
The Future of Web Scraping Technology
As technology continuously evolves, so too does the field of web scraping. With advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning, future scraping tools are expected to become smarter, identifying and extracting data with increased precision. These technologies will allow for more complex data mining operations that can adapt to changes in website structures, making it easier for businesses to collect and analyze vast amounts of data.
Furthermore, as web scraping faces ongoing challenges, including increased protection measures by websites, the development of more sophisticated evasion techniques and tools will likely emerge. The integration of AI-driven strategies can enhance the effectiveness of scraping efforts while maintaining ethical standards, ensuring that the industry adapts to both technological advancements and ethical considerations.
Building a Robust Web Scraping Strategy
Creating a robust web scraping strategy involves combining technical expertise with well-defined objectives and business needs. Before launching scraping activities, businesses should outline clear goals regarding what data is needed and how it will be used. This approach enables targeted scraping efforts and helps in selecting appropriate tools and methodologies.
Furthermore, regular monitoring and maintenance of scraping setups are essential to ensure data accuracy and compliance with legal requirements. By establishing automated checks and feedback loops, organizations can maintain the integrity of their data collection processes. Developing a comprehensive scraping strategy not only enhances data quality but also supports sustainable business growth through insightful data analysis.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does web scraping work?
Web scraping works by sending an HTTP request to a target webpage, receiving its HTML content, and then using a parser to navigate and extract the necessary data from that content. This process typically involves identifying specific HTML elements like tags, classes, or IDs to accurately gather the desired information.
What are the main applications of web scraping?
Web scraping has several applications including market research for competitors and pricing analysis, news aggregation for comparing articles across sources, and extracting real estate listings from property websites. These applications leverage web scraping to automate data collection and analysis.
What data extraction techniques are commonly used in web scraping?
Common data extraction techniques in web scraping include using libraries like BeautifulSoup or Scrapy for parsing HTML, regular expressions for identifying patterns in text, and API calls when available. These techniques help efficiently extract required data while navigating diverse website structures.
Is ethical web scraping possible?
Yes, ethical web scraping is possible by adhering to a website’s `robots.txt` file and its terms of service. Ensuring compliance with these guidelines, along with respectful rate limiting and responsible data use, can make web scraping a legitimate practice.
What are some popular web scraping tools?
Popular web scraping tools include BeautifulSoup, Scrapy, Selenium, and Puppeteer. These tools provide various functionalities that simplify the process of web scraping, from data extraction to automation of interactions with dynamic websites.
| Key Point | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | Web scraping is a technique to extract data from websites. |
| Process | 1. Sending a request to the server 2. Receiving the HTML response 3. Parsing HTML content 4. Extracting desired data 5. Storing the data in formats like CSV or JSON. |
| Applications | Used for market research, news aggregation, real estate listings, etc. |
| Considerations | Includes legal implications, rate limiting, and ensuring data accuracy. |
Summary
Web scraping is a valuable technique for gathering data from the internet efficiently. By understanding the methodology behind web scraping, including how to send requests, parse data, and store information, users can apply this technology across various fields such as market research and news aggregation. However, it’s crucial to remain aware of legal aspects and ethical practices to ensure responsible use of web scraping.