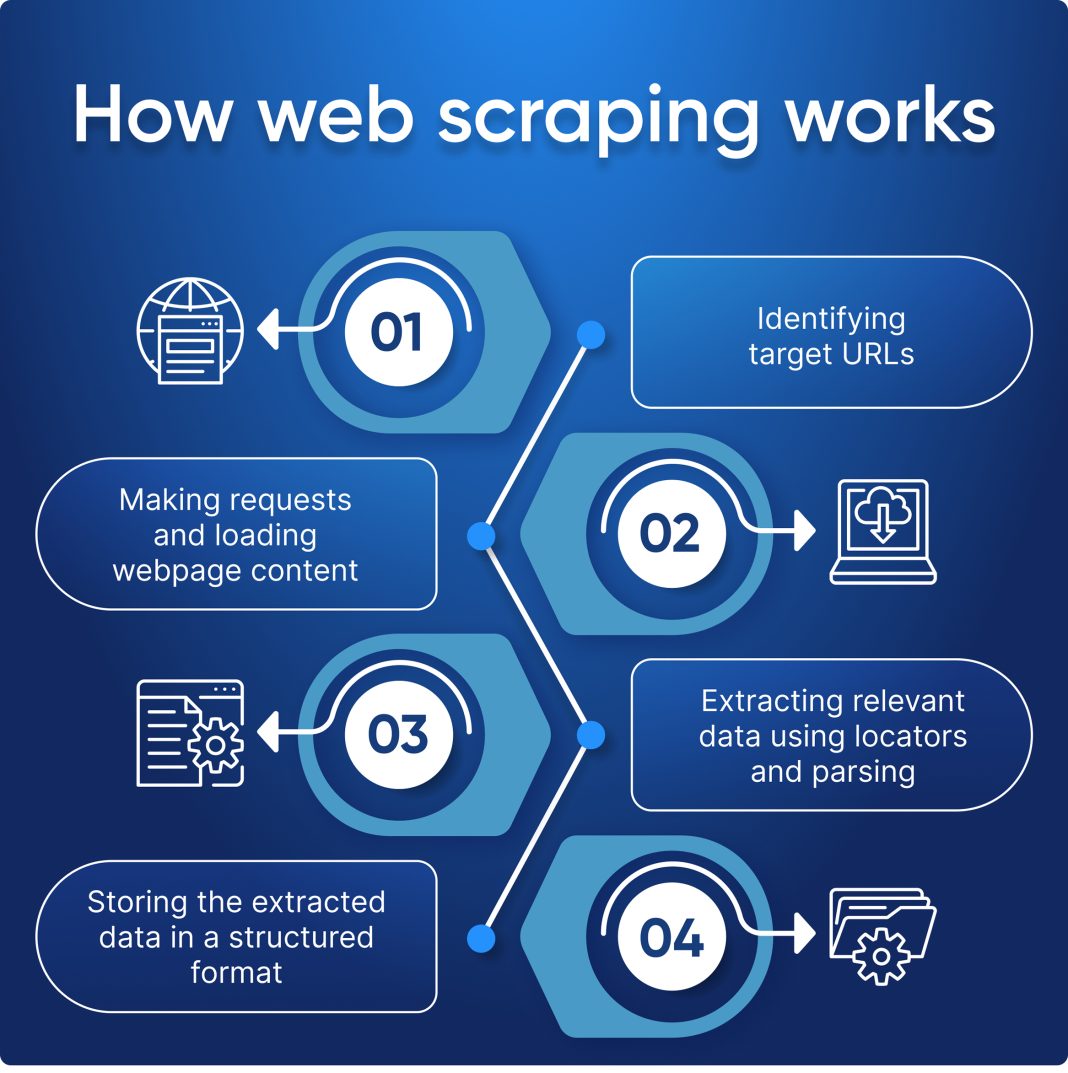
Web scraping is a powerful technique for data extraction that allows individuals and businesses to gather valuable information from websites. By utilizing web crawlers and HTML parsing methods, users can automate the process of fetching web pages and extracting pertinent data efficiently. With the rise of big data and the growing importance of market research, web scraping has become an essential skill for analysts and developers alike. Numerous Python libraries for scraping, such as Beautiful Soup and Scrapy, facilitate this process, making it more accessible to a broader audience. However, ethical web scraping practices must be observed to avoid potential legal issues and ensure that the integrity of the extracted data is maintained.
The art of web data extraction, often referred to as online data mining, involves obtaining information from web resources by means of advanced programming techniques. This practice is embraced by many as it compels individuals to harness the potential of automated systems to survey vast amounts of data efficiently. Utilizing tools for HTML document manipulation and understanding the mechanics of web crawlers play a critical role in this process. Moreover, techniques surrounding ethical data collection are crucial, ensuring compliance with site rules and usage constraints. Whether termed data scraping or content harvesting, the core principles remain centered on extracting and parsing information, unlocking the vast data landscape of the internet.
The Importance of HTML Parsing in Web Scraping
HTML parsing is a fundamental component of web scraping that enables the extraction of specific information from web pages. It involves breaking down the HTML structure into manageable pieces, allowing developers to access the information they need. Understanding the Document Object Model (DOM) is crucial here, as it represents the structure of web content in a tree-like format. By navigating through this structure, one can effectively locate and extract data points such as text, links, images, and more.
Moreover, various Python libraries such as Beautiful Soup and lxml are designed to simplify the HTML parsing process. Beautiful Soup, for instance, provides an intuitive syntax that allows developers to easily navigate and manipulate HTML documents. This makes it an ideal choice for both novice and experienced programmers looking to scrape data efficiently. Ultimately, mastering HTML parsing is essential for anyone looking to harness the power of web scraping.
Using Web Crawlers for Efficient Data Extraction
Web crawlers, also known as web spiders, are automated bots that systematically browse the internet to collect data from websites. They play a crucial role in web scraping by allowing users to gather large volumes of data across multiple pages or entire sites. Crawlers follow links from one page to another, making it possible to scrape dynamic or static content efficiently. Additionally, they can be programmed to scrape only specific types of content, such as images, text, or even metadata.
The significance of web crawlers in large-scale data extraction cannot be overstated. They can be built using frameworks like Scrapy, which offers powerful functionalities for managing crawling tasks, such as handling requests, following links, and storing data. This means that businesses and researchers can gather insights from entire datasets without manual intervention, streamlining the data extraction process and enhancing productivity. As such, mastering the use of web crawlers is a vital skill for professionals involved in data analysis.
Best Python Libraries for Web Scraping Projects
Python is widely regarded as one of the best programming languages for web scraping projects, primarily due to its rich ecosystem of libraries designed for this purpose. Beautiful Soup, for instance, excels in HTML parsing, making it easy to extract data from complex web pages. Similarly, Scrapy is an open-source framework that provides a comprehensive environment for building web crawlers. These libraries not only simplify the scraping process but also enhance the efficiency and accuracy of data extraction.
In addition to Beautiful Soup and Scrapy, Selenium is another powerful tool, particularly when dealing with dynamic web content that relies on JavaScript. It allows developers to automate web browsers and interact with web applications as a human would, making it invaluable for scraping data that is not readily available in the HTML source. By exploring and utilizing these Python libraries, developers can streamline their web scraping workflows and achieve more reliable results.
Ethical Web Scraping Practices for Data Collection
Ethical web scraping practices are essential to ensure that data extraction activities comply with legal and moral standards. One of the primary considerations is adhering to the website’s robots.txt file, which outlines the rules that govern how web crawlers should interact with the site. This file indicates which parts of the website are accessible for crawling and which parts should be avoided, helping to prevent potential legal issues and preserving the integrity of the website.
In addition to respecting robots.txt, it’s also important to implement polite scraping techniques. This includes limiting the number of requests sent to a server and incorporating delays between requests to avoid overwhelming the website’s resources. By practicing ethical web scraping, developers not only avoid the risk of being banned but also contribute positively to the broader online ecosystem. Engaging in ethical scraping helps maintain goodwill between web developers and website owners.
Challenges of Web Scraping and How to Overcome Them
Web scraping, while a powerful tool for data collection, does come with its set of challenges. Websites often employ anti-scraping techniques such as CAPTCHAs, IP blocking, and changes in HTML structure to protect their data. These obstacles can hinder effective data extraction, making it essential for developers to adopt strategies to overcome them. For instance, using rotating proxies can help to mitigate IP blocking by changing the IP signature with each request, allowing for more sustained access to the targeted website.
Additionally, the dynamic nature of many websites can be problematic, as changes to the site’s layout or structure can break existing scraping scripts. It is essential to build resilient web scraping solutions that can quickly adapt to these changes. Leveraging libraries like Selenium can assist in managing dynamic content while continuously monitoring the sites for modifications can alert developers to necessary updates. By understanding and preparing for these challenges, data professionals can ensure the success of their web scraping initiatives.
Data Extraction Techniques in Web Scraping
Data extraction is a critical phase in the web scraping process that determines how effectively raw data is collected from HTML documents. This phase typically involves identifying and isolating the data points of interest, such as product prices, reviews, or contact information, and then capturing them in a structured format. Techniques such as XPath or CSS selectors offer powerful ways to navigate through HTML elements and retrieve the desired data efficiently.
In addition to static data extraction techniques, advanced approaches such as machine learning algorithms can also be employed to enhance the accuracy of data collection and extraction. By training models to recognize patterns in data presentation and make inferences, developers can automate the extraction process even further. Understanding these diverse data extraction techniques will allow web scraping professionals to efficiently convert unstructured web data into organized datasets ready for analysis.
The Role of Data Privacy in Ethical Web Scraping
As web scraping becomes increasingly prevalent, concerns surrounding data privacy have come to the forefront. When scraping data from websites that may contain personal information, it’s imperative to consider the legal implications and ethical responsibilities of handling such data. Compliance with regulations like GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) is crucial, as it sets tight boundaries on how personal data can be collected, processed, and shared.
Being transparent in the scraping process and ensuring data is gathered without infringing on individual rights should be a priority for anyone engaged in web scraping. Additionally, anonymizing data and using encryption to protect sensitive information during storage and transfer are practices that help bolster data privacy. By implementing these strategies, web scraping professionals can champion ethical standards in data collection while cultivating trust with users and websites alike.
Future Trends in Web Scraping Technology
The field of web scraping is continuously evolving, influenced by advances in technology and the growing complexity of web services. As websites increasingly utilize dynamic content and sophisticated user interfaces, the demand for more robust scraping tools is on the rise. In the future, we can expect to see enhancements in scraping frameworks that incorporate artificial intelligence and machine learning to better navigate and extract data from challenging environments, such as single-page applications.
Furthermore, with the growing emphasis on data ethics, there are likely to be more regulations guiding the practice of web scraping. Developers and companies will need to stay informed about these changes and prioritize ethical scraping practices while also leveraging the latest tools and technologies. By adapting to these shifts, data professionals will be well-positioned to harness the full potential of web scraping as a powerful data collection method.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is web scraping and how is it used for data extraction?
Web scraping is the process of extracting data from websites. It involves fetching web pages and systematically extracting specific information from them. This technique is widely used for data extraction in various fields like data analysis and market research.
What are the common tools and Python libraries for web scraping?
Common tools and Python libraries for web scraping include Beautiful Soup, which is used for HTML parsing, Scrapy, a web-crawling framework, and Selenium, which allows for automated scraping of dynamic content. These tools enhance efficiency in data extraction.
How do web crawlers function in the web scraping process?
Web crawlers are automated programs that browse the internet, downloading web pages to gather data. They play a crucial role in the web scraping process by enabling the collection of large amounts of data from multiple websites.
What is HTML parsing in the context of web scraping?
HTML parsing refers to analyzing the structure of web pages composed of HTML elements to extract the desired information. Libraries such as Beautiful Soup in Python are commonly used for HTML parsing, making the data extraction process easier.
What are the ethical considerations to keep in mind while web scraping?
When engaging in web scraping, it is essential to practice ethical web scraping. This includes respecting the website’s robots.txt file, which sets rules for web crawlers, and avoiding overwhelming servers with too many requests, which can lead to IP bans.
| Key Concept | Description |
|---|---|
| HTML Structure | Understanding the structure of HTML elements to locate the data for extraction. |
| Crawlers | Programs that browse and download web pages automatically for data scraping. |
| Parsing | Analyzing fetched web pages to extract required information using parsing libraries like Beautiful Soup. |
| Beautiful Soup | A Python library for parsing HTML and XML documents. |
| Scrapy | An open-source web-crawling framework for Python. |
| Selenium | A tool for automated web applications, useful for scraping dynamic content. |
| Ethics of Web Scraping | Important to follow ethical guidelines and respect websites’ robots.txt file to avoid bans. |
Summary
Web scraping is an essential technique for gathering data efficiently from online sources. By leveraging various tools and libraries like Beautiful Soup, Scrapy, and Selenium, along with an understanding of HTML structure and ethical practices, individuals and organizations can effectively extract valuable insights from the web.