Web scraping is a powerful tool that enables users to extract valuable data from websites quickly and efficiently. As we delve into what web scraping encompasses, it becomes clear that this technique has numerous applications, from compiling product prices for e-commerce businesses to aggregating news articles from various sources. For those new to this practice, our beginner’s web scraping guide will illuminate essential web scraping techniques and provide a clear pathway on how to start web scraping effectively. It’s crucial to be aware of the potential legal issues in web scraping, as many websites have specific regulations that govern how data can be collected. In this comprehensive guide, you’ll learn not just the ‘how-to’ but also the importance of ethical considerations when scraping data from the web.
Data extraction from online sources, often referred to as data scraping or web harvesting, harnesses the power of technology to gather information meticulously. This process helps businesses and individuals alike to monitor market trends, analyze competitor pricing, or aggregate data for research purposes. Aspiring scrapers can benefit greatly from a thorough understanding of available web scraping techniques, ensuring they navigate the complexities of this field. By familiarizing themselves with the beginner’s web scraping guide, newcomers can safely dive into the world of data collection while also adhering to legal standards. Ultimately, mastering online data retrieval opens up a myriad of opportunities across various industries.
Understanding the Basics of Web Scraping
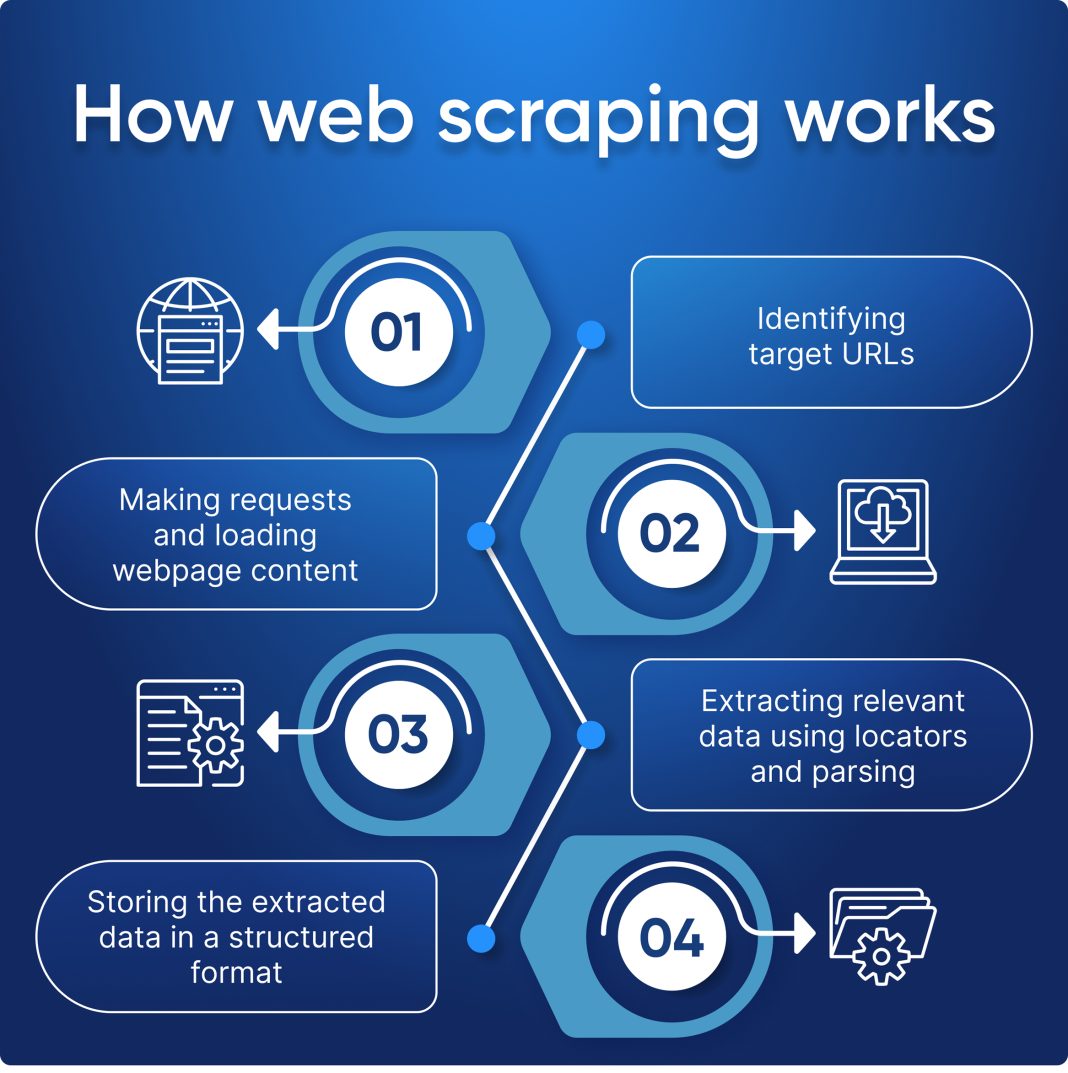
Web scraping, fundamentally, is a technique used to automate the collection of data from the internet. It involves fetching web pages and extracting useful information from them. This process can be applied across various domains, enabling users to gather data like product prices or real estate listings efficiently. Moreover, understanding web scraping is essential for beginners looking to leverage data for decision-making and analytical purposes in their projects.
When discussing the basics, it’s important to note that web scraping typically involves using programming languages such as Python, combined with libraries that help parse HTML code. With tools like BeautifulSoup and Requests, newcomers can learn how to scrape data effectively. As you delve deeper, you’ll discover various techniques tailored for different types of websites and data, allowing you to customize your approach.
Popular Web Scraping Techniques
There are various techniques to perform web scraping that cater to different needs and complexities. One common method is using a library like BeautifulSoup in Python to scrape static HTML content. This technique is straightforward and works well for many websites. Additionally, developers often implement web automation tools, such as Selenium, which is particularly useful when dealing with dynamic content generated by JavaScript.
Another popular technique is the use of APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) when available. Many websites provide APIs that allow you to access their data in a structured format without the need for scraping. This approach is not only more reliable but also reduces potential conflicts with the website owners, making it a preferred method when possible.
How to Start Web Scraping for Beginners
Starting your journey in web scraping is easier than it seems. First, familiarize yourself with a programming language, preferably Python, known for its simplicity and extensive libraries for web scraping tasks. Once you have a grasp of Python, install necessary libraries such as BeautifulSoup and Requests to handle data retrieval and parsing effectively.
Next, choose a target website and analyze its structure to identify the information you want to scrape. Begin with a basic script that makes an HTTP request to the site and retrieves the HTML content. Don’t forget to parse the HTML data to fetch the specific elements you need, such as product names or prices. As you become more comfortable, you can experiment with more complex techniques, including handling pagination or dealing with CAPTCHA challenges.
Legal Issues in Web Scraping
Before you embark on web scraping, it’s crucial to understand the legal landscape surrounding this practice. Each website has its own terms of service, which may include explicit prohibitions against scraping. Reviewing the site’s robots.txt file can provide guidance on which areas of the site can be scraped and which should be avoided. Compliance with legal standards is not just prudent; it’s necessary to avoid potential litigation or blocking.
Additionally, laws around data privacy and intellectual property rights can also affect your scraping activities. Depending on your jurisdiction, regulations like the GDPR in Europe may impose restrictions on how data can be collected and used. Thus, it’s wise for developers to educate themselves about these legal issues before engaging in web scraping.
Tools and Libraries for Effective Web Scraping
There are numerous tools and libraries available to streamline the web scraping process, making it easier for beginners to get started. Python, being the go-to programming language for web scraping, offers an array of libraries such as Scrapy, a powerful and efficient framework. Scrapy allows you to scrape websites and manage requests seamlessly, making it a favorite among advanced users.
In addition to Scrapy, tools like Selenium can automate web browsers to scrape dynamic web content that changes based on user interactions. These tools not only enhance your scraping capabilities but also ensure you can extract data from various types of websites. By leveraging the right tools, even beginners can execute complex scraping tasks effectively.
Best Practices for Web Scraping
When engaging in web scraping, following best practices can make your efforts more effective and sustainable. Start by respecting the target website’s scraping policies outlined in its robots.txt file. This file indicates the rules regarding which parts of the site can be accessed by automated agents, ensuring your scraping activities do not violate copyrighted material or other web rights.
Additionally, implement rate limiting in your scraping scripts to avoid overwhelming the server with requests. Sending too many requests in a short period can lead to your IP being banned. A good rule of thumb is to introduce delays between requests, mimicking human browsing behavior. By adhering to these best practices, you not only protect your scraping efforts but also maintain a positive relationship with the websites you interact with.
Challenges in Web Scraping to Watch Out For
While web scraping opens up vast opportunities for data collection, it also comes with its own set of challenges. One significant hurdle is the variability in website structures; as web technologies evolve, so do web pages. Changes in HTML or JavaScript can break existing scraping scripts, requiring constant updates and maintenance.
Additionally, many sites employ anti-scraping measures, such as CAPTCHAs or IP blocking, to protect their content. Navigating these obstacles requires a combination of technical skills and creativity, ensuring that your scraper can adapt to changing conditions without losing effectiveness.
Ethical Web Scraping: Understanding the Boundaries
Ethics play a crucial role in web scraping. While the technical aspects might be straightforward, understanding the moral implications of scraping is essential. Scraping for malicious intents, such as data theft or spamming, falls into unethical practices, which can lead to serious consequences.
Instead, focus on respectful engagements with the web content. If a website provides an API, consider using it instead of scraping, as this shows respect for the site’s operational integrity. Additionally, it’s always a good practice to give credit for the data you use and comply with any licensing agreements.
Future Trends in Web Scraping
As technology advances, the world of web scraping continues to evolve, with emerging trends shaping how data is collected. One noteworthy trend is the increasing use of artificial intelligence and machine learning in web scraping processes. These technologies enable more efficient data extraction and analysis, allowing scrapers to gather insights from large datasets quickly and accurately.
Moreover, with the rise in privacy concerns and regulations, there will be an increasing emphasis on ethical scraping techniques. Future web scrapers will need to be versatile, adapting not only to technological advancements but also to the shifting legal and ethical landscape of digital data collection.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is web scraping?
Web scraping is the automated technique used to extract data from websites. It involves retrieving the HTML content of web pages and parsing this data to obtain valuable information. This method is widely used for applications like price comparison, market research, and data collection.
How do I start web scraping as a beginner?
To start web scraping, you need basic programming knowledge, preferably in Python. First, install libraries like BeautifulSoup and Requests, choose a website to scrape, write a code snippet to make HTTP requests, parse the HTML response, and finally save the derived data in formats like CSV or JSON.
What are some common web scraping techniques?
Common web scraping techniques include using libraries such as BeautifulSoup for HTML parsing, Selenium for navigating dynamic web pages, and Scrapy for large-scale scraping projects. Each technique can be chosen based on the specific requirements of the data extraction task.
What are the legal issues in web scraping that I should be aware of?
Legal issues in web scraping involve adhering to a website’s terms of service and respecting its robots.txt file, which indicates scraping permissions. Violating these could lead to legal actions. It’s essential to stay informed about copyright and data protection laws relative to the data you scrape.
Why is understanding web scraping important for data collection?
Understanding web scraping is crucial for effective data collection as it allows individuals and businesses to automate the gathering of information from the web. By leveraging web scraping, you can quickly aggregate data for analysis, enhance research accuracy, and improve decision-making across various sectors.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| What is Web Scraping? | The process of extracting data programmatically from websites by retrieving HTML content and parsing it. |
| Common Uses | Used for price comparison, market research, data collection for machine learning, and monitoring changes on websites. |
| Getting Started | 1. Install libraries (BeautifulSoup, Requests) 2. Choose a target website 3. Make HTTP requests 4. Parse HTML data 5. Store data in formats like CSV or JSON |
| Legal Considerations | Review the robots.txt file of the website and understand legal implications, as some sites may prohibit scraping. |
Summary
Web scraping is a crucial technique for data extraction from websites in today’s digital landscape. This guide provides a foundational understanding of what web scraping is, its applications, and how to embark on your web scraping journey. By mastering web scraping, you can unlock a wealth of data that can facilitate informed decisions, enhance your research, or even power your next big project. Always remember the ethical and legal boundaries associated with web scraping to ensure responsible data use.