Web scraping is a powerful and versatile technique that allows individuals and businesses to extract vast amounts of data from websites quickly and efficiently. By utilizing various web scraping tools and techniques, users can automate the process of data extraction, making it easier to gather information for analysis or decision-making. Python web scraping has gained immense popularity due to its simplicity and the availability of robust libraries like BeautifulSoup and Scrapy that streamline the scraping process. This approach not only saves time but also enhances the accuracy of collected data, which can be crucial for tasks like competitive analysis or market research. However, it’s essential to engage in ethical web scraping practices to respect a website’s terms of service and ensure responsible use of the information acquired.
Data harvesting from the internet, often referred to as data scraping, is an indispensable tool for anyone seeking to gather information efficiently. This method involves parsing web pages to pull out specific details, helping businesses perform tasks like market research and trend analysis. Many users opt for popular programming languages, particularly Python, due to its extensive support for various web scraping libraries that simplify the data extraction process. Additionally, as online content continues to grow, mastering web crawling techniques becomes increasingly valuable for maintaining a competitive edge. Nonetheless, it’s crucial to navigate the landscape of information collection with awareness of legal boundaries and ethical considerations.
What is Web Scraping?
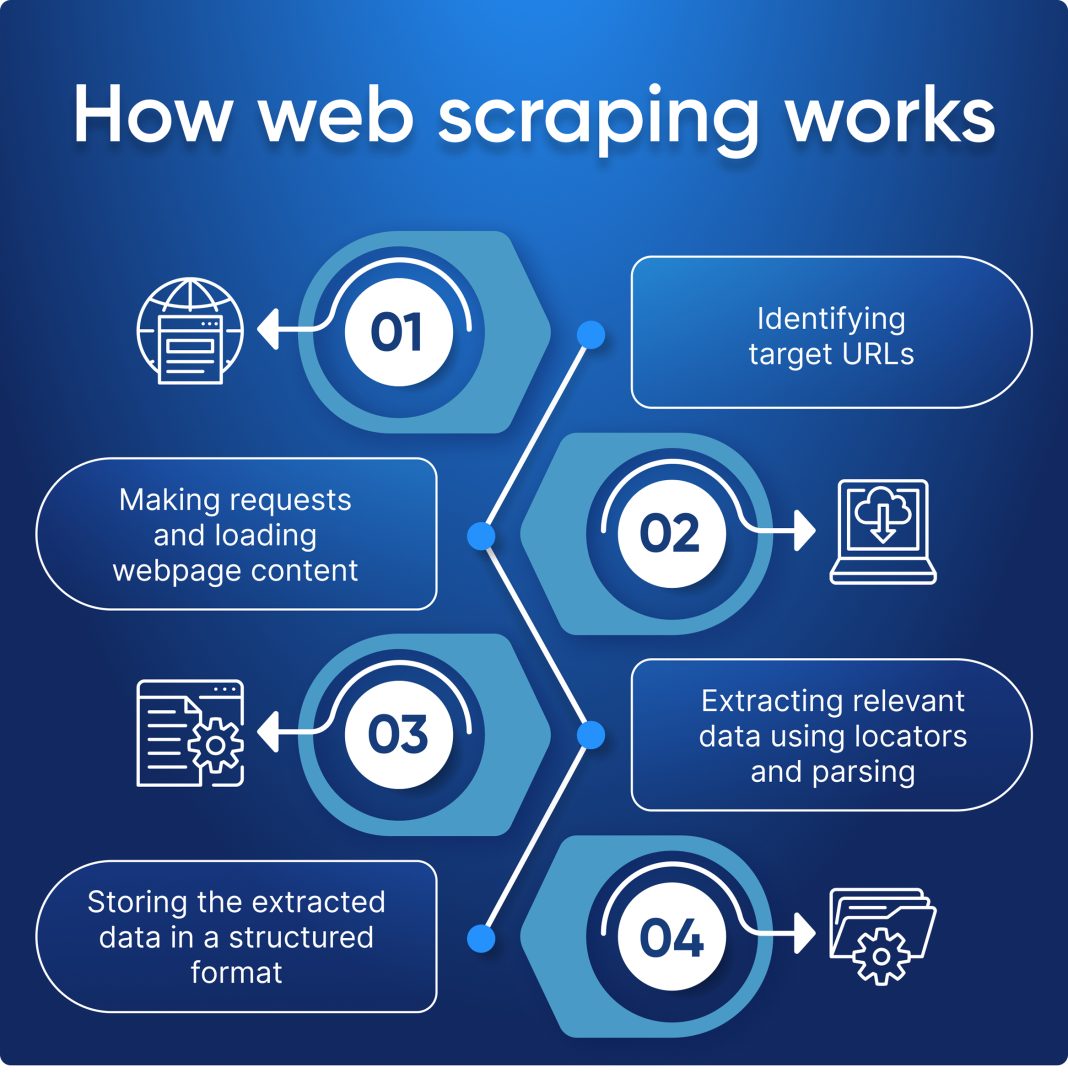
Web scraping is a powerful technique that enables users to automatically gather and analyze data from web pages. This method typically involves sending requests to web servers, receiving HTML content, and then parsing that content to extract relevant information like pricing, product details, or user reviews. One of the reasons web scraping has gained popularity is due to the vast amount of data available on the internet that can be harvested for various purposes.
The process usually begins with identifying the target website and the specific data needed. Following that, developers can utilize various programming tools to script the scraping process. While this may sound simple, it’s crucial for users to be aware of the technical complexities involved, such as managing cookies, navigating web sessions, and handling JavaScript-rendered content.
Key Web Scraping Techniques
There are several web scraping techniques that can help optimize the data extraction process. One common approach is to use the Document Object Model (DOM) to traverse the HTML structure of a webpage. This method often utilizes libraries such as BeautifulSoup in Python, which allow developers to easily navigate through the different elements to find and extract desired data efficiently. Additionally, using APIs provided by websites can greatly enhance the web scraping experience by offering structured data, although this alternative may require subscribing to specific services.
Another effective technique is employing headless browsers, which simulate user interaction with web pages. This method is particularly useful for scraping dynamic content that requires JavaScript execution to display accurately. Tools like Selenium can automate web browsers and enable users to scrape content that wouldn’t otherwise be accessible by standard scraping methods.
The Role of Python in Web Scraping
Python has established itself as the leading programming language for web scraping, owing to its simplicity and a robust ecosystem of libraries. Notable libraries such as Scrapy and Beautiful Soup simplify the process of fetching, parsing, and storing scraped data. Scrapy, for instance, is a powerful framework that handles requests, provides built-in support for following links, and offers handling for various formats of output such as JSON or CSV, making it an ideal choice for larger projects.
Furthermore, Python’s ability to integrate with data analysis libraries, like Pandas and NumPy, allows developers to not only scrape data but also perform in-depth analysis and data manipulation post-extraction. This integration streamlines the workflow, making it straightforward to transition from data extraction to actionable insights.
Ethical Considerations in Web Scraping
While web scraping offers significant advantages, it is essential to navigate the ethical landscape thoughtfully. Many websites have specific terms of service that prohibit scraping, and failing to adhere to these guidelines can lead to legal repercussions. It’s crucial to approach web scraping with respect for the data owners and their rights.
Another important ethical consideration is rate limiting, which involves controlling the frequency of requests sent to a server. This practice prevents overwhelming a website’s infrastructure and ensures that the scraper behaves like a normal user. Models of ethical web scraping often advocate for transparency and proper attribution to the data sources when utilized in research or commercial applications.
Popular Web Scraping Tools
There are numerous tools available for web scraping, enabling both novices and experienced developers to extract data efficiently. Tools like Octoparse and ParseHub provide user-friendly interfaces and visual scraping capabilities, eliminating the need for extensive programming knowledge. These platforms often include built-in proxies to help users navigate through anti-scraping measures employed by many websites.
For those seeking advanced functionalities, frameworks such as Apify and Scrapy remain at the forefront. They offer comprehensive solutions for building scalable web scrapers, complete with features for handling session management and dealing with captcha challenges. Selecting the right tool often depends on the user’s specific needs, whether it’s rapid prototyping or developing complex data extraction solutions.
Applications of Web Scraping
Web scraping has a diverse range of applications across various industries. In business, companies leverage scraping techniques to conduct competitive analysis, allowing them to monitor competitors’ pricing, product offerings, and marketing strategies. This information can provide a competitive edge by facilitating informed decision-making.
In the realm of research, scholars and analysts use web scraping to compile large datasets from numerous online sources. This can include academic publications, social media analyses, or economic data trends, all of which contribute to enriching their studies and findings.
Understanding Data Extraction
Data extraction is a critical part of the web scraping process, enabling users to gather structured information from unstructured or semi-structured web content. With the vast amount of data generated daily, effective data extraction techniques are paramount for transforming raw data into usable formats. This can range from parsing HTML to cleaning and filtering the extracted information.
Techniques such as XPath and CSS selectors play an integral role in accurately extracting relevant data points from web pages. By utilizing these tools, developers can create efficient and precise scripts that minimize errors and enhance the accuracy of the data collection process.
The Future of Web Scraping
As technology evolves, so too will the methods and tools associated with web scraping. The rise of artificial intelligence and machine learning is likely to refine how data is extracted, thereby increasing the efficiency and effectiveness of scraping tasks. For instance, AI algorithms could automate the identification of relevant data points and help discern patterns or trends within the scraped datasets.
Moreover, as more organizations recognize the value of data, there’s an anticipated increase in ethical scraping initiatives. This shift will encourage the development of standards and best practices to foster collaboration between data scrapers and website owners, ensuring a mutually beneficial relationship.
Challenges in Web Scraping
While web scraping can be a rewarding endeavor, it is not without its challenges. Many websites implement security measures such as rate limiting, CAPTCHAs, and frequent changes to their layout to thwart automated scraping attempts. These obstacles require developers to constantly adapt their scraping techniques and tools to remain effective.
Additionally, the legal landscape surrounding web scraping can be complex, with varying regulations across different countries and industries. This necessitates that individuals and businesses engaging in web scraping conduct thorough research on applicable laws and ethical standards to avoid potential legal issues.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is web scraping and how does it work?
Web scraping is a technique that allows users to extract large amounts of data from websites quickly. It works by fetching a website’s content, parsing the HTML or XML structure, and extracting specific information using programming tools or libraries, such as Python’s BeautifulSoup or Scrapy.
What are some effective web scraping techniques?
Effective web scraping techniques include using HTML parsing to extract data elements, employing Xpath and CSS selectors for precise targeting, and implementing automated scripts that can navigate through pages. Libraries like BeautifulSoup and Scrapy in Python are popular for these techniques.
What are the most popular Python web scraping tools?
The most popular Python web scraping tools include BeautifulSoup for parsing HTML, Scrapy for creating fully featured web crawlers, and Requests for handling HTTP requests. Each tool offers unique functionalities to facilitate efficient data extraction.
Is ethical web scraping important, and why?
Ethical web scraping is crucial as it respects the legal boundaries and terms of service set by websites. By practicing ethical web scraping, such as obtaining permission and avoiding excessive requests, scrapers ensure they do not disrupt a website’s operations and maintain good relationships.
How can I ensure my web scraping is legal?
To ensure your web scraping is legal, always check the website’s terms of service to see if scraping is permitted. Additionally, comply with robots.txt directives and consider the data privacy laws that may impact your data extraction activities.
What are some use cases for data extraction through web scraping?
Data extraction through web scraping is widely used in various fields, such as collecting market research data, monitoring product prices for e-commerce, aggregating real estate listings for analysis, and tracking competitor activities to improve business strategies.
How can I avoid getting blocked while web scraping?
To avoid getting blocked while web scraping, implement practices like rate limiting your requests, using user-agent rotation, and keeping session cookies to mimic human-like browsing behavior. These practices help you stay under the radar of website defenses.
Can web scraping be done without coding?
Yes, web scraping can be done without coding by using web scraping tools that offer visual interfaces, such as Octoparse or ParseHub. These tools allow users to create scraping workflows through point-and-click actions without the need for programming knowledge.
What are the limitations of web scraping?
Limitations of web scraping include potential legal issues, challenges with dynamic websites that load data via JavaScript, and the possibility of websites implementing anti-scraping measures. Additionally, extracted data may need further processing to be useful.
How do I get started with web scraping using Python?
To get started with web scraping using Python, install essential libraries like Requests and BeautifulSoup, then practice writing simple scripts to fetch web pages and extract data. Online tutorials and documentation provide helpful guidance for beginners.
| Key Point | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | Web scraping is a technique used to extract large amounts of data from websites. |
| Automation | Web scraping can be automated using programming languages like Python, which has libraries such as BeautifulSoup and Scrapy. |
| Common Uses | Common uses include data collection, competitive analysis, real estate aggregation, and price monitoring. |
| Legal Considerations | Legal and ethical considerations are important; always check a website’s terms of service before scraping. |
| Best Practices | Implement best practices such as rate limiting to avoid overwhelming the server. |
Summary
Web scraping is a powerful technique that allows users to efficiently gather data from various websites for different applications. By leveraging tools and programming languages, especially Python, users can automate this data extraction process. However, it’s crucial to remain aware of the legal frameworks and ethical guidelines associated with web scraping to ensure compliance and responsible data usage.